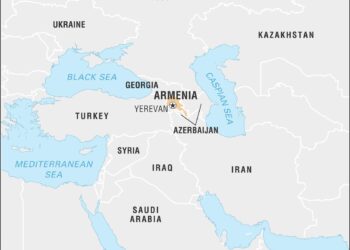
In recent years, the geopolitical landscape of the South Caucasus has been significantly influenced by the long-standing conflict between armenia and azerbaijan, especially over the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh. Despite attempts to establish a sustainable peace following the 2020 war, tensions remain high as both nations grapple with ancient grievances, national identity, and territorial aspirations. This article explores the complexities of the peace process, highlighting the key obstacles and recent developments that continue to stymie reconciliation efforts. By examining the role of external actors, the impact of domestic politics, and the evolving dynamic on the ground, we aim to provide a thorough overview of the current state of affairs between Armenia and Azerbaijan, shedding light on the precarious balance of power in the region. As both countries navigate this fraught terrain, the quest for lasting peace appears as elusive as ever, raising pressing questions about the future stability of the south Caucasus.
Armenia and Azerbaijan: Historical Context of Ongoing Tensions

The roots of the enduring conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan trace back to the early 20th century,fraught with historical grievances and nationalistic fervor. The dissolution of the Soviet Union in the late 1980s intensified territorial disputes, particularly over Nagorno-Karabakh, a region predominantly populated by ethnic Armenians but internationally recognized as part of Azerbaijan.The subsequent war from 1988 to 1994 resulted in significant territorial changes and deep-seated animosities, as both nations suffered heavy casualties and displacement of populations. Today, the residue of that war continues to impact diplomatic relations, with national identity and territorial integrity at the forefront of both countries’ political discourses.
In recent years, various rounds of negotiations have attempted to broker peace; however, these dialogues often falter amid military skirmishes and hardline rhetoric. the geopolitical landscape further complicates the situation, as external powers, including Russia and Turkey, hold vested interests that influence both the peace process and escalations in conflict. To better understand this dynamic, we can summarize some key factors that contribute to the ongoing tensions:
- Historical Grievances: Memories of conflict linger, shaping public perception and political will.
- Territorial Claims: Both nations lay claim to the Nagorno-Karabakh region, igniting nationalistic fervor.
- Geopolitical Influences: The involvement of regional powers adds layers of complexity to peace negotiations.
- Diverse Political Objectives: Each country’s leadership navigates internal pressures and external expectations,impacting peace efforts.
Challenges in the Current Peace Process and Diplomatic Efforts

The peace process between Armenia and Azerbaijan has encountered several significant obstacles, impeding diplomatic efforts aimed at achieving long-term stability in the region. The underlying issues, rooted in historical grievances and territorial disputes, continue to fuel tensions. Key challenges include:
- National Identity: Both nations have strong nationalistic sentiments tied to the conflict, making concessions politically sensitive.
- Territorial Integrity: Disagreements over borders, particularly regarding nagorno-Karabakh, persist, complicating negotiations.
- External Influence: Involvement from regional powers like russia and Turkey often skews the process,reflecting their strategic interests rather than genuine peace.
Furthermore, the lack of trust between the parties exacerbates the situation, leading to stalled dialogues and repeated flare-ups. Each side remains skeptical of the other’s intentions, and previous ceasefires have frequently been violated. Critical factors impacting the peace process include:
- Military Posturing: Continuous military engagements undermine confidence-building measures.
- Political instability: Internal political dynamics within both countries can derail negotiations and shift priorities.
- Societal Divides: Deep-seated animosities among the populations hinder the acceptance of any compromise solutions.
The Role of International Actors in Mediating Conflicts

The involvement of international actors in the Armenia-Azerbaijan conflict has been pivotal,particularly as tensions flare over the Nagorno-Karabakh region.Key mediators such as the OSCE Minsk Group, consisting of the United states, France, and Russia, have long sought to facilitate discussions between the two nations. Their diplomatic efforts aim to establish a framework for peace, though a prosperous resolution has remained elusive. Despite multiple rounds of negotiations, the parties have struggled to find common ground, frequently enough undermined by longstanding historical grievances and nationalism. The influence of these international actors hinges on their ability to maintain neutrality while offering balanced proposals that address the concerns of both sides.
Additionally, the role of regional players cannot be underestimated. Nations such as Turkey and Iran have interests in the conflict that frequently enough complicate mediation efforts. As an example, Turkey’s support of Azerbaijan has bolstered the latter’s position in negotiations, whereas Iran has expressed concern over ethnic and territorial issues that could impact its own stability. This multi-faceted involvement presents both opportunities and challenges for conflict resolution, as it underscores the importance of comprehensive dialog. In light of these complexities, a more cohesive international strategy that includes a broader spectrum of stakeholders might be essential for achieving lasting peace in the region.
Humanitarian Impacts and the Need for Civil Society Engagement

The ongoing tensions between Armenia and Azerbaijan have profound humanitarian consequences that extend beyond political disputes. In areas affected by conflict, civilian populations grapple with dire conditions, including displacement, food insecurity, and mental health challenges. The blockade of essential resources exacerbates these vulnerabilities, as communities find it increasingly difficult to access basic services.Moreover, the psychological toll on these populations cannot be understated; prolonged exposure to conflict can lead to intergenerational trauma, altering the social fabric and hindering long-term recovery.
To address these pressing humanitarian needs effectively, civil society engagement emerges as a critical component of the peace process. Grassroots organizations and local activists play a vital role in mobilizing resources, advocating for human rights, and fostering dialogue among affected communities. Their grassroots efforts can bridge gaps between conflicting parties and promote shared understanding. Importantly, the involvement of civil society can lead to innovative solutions that empower local populations to contribute to their own healing and rebuilding efforts, thus ensuring a more sustainable and inclusive peace framework. The challenges are significant, but collaborative efforts driven by civil society are essential for fostering resilience amid uncertainty.
Recommendations for Sustainable Peacebuilding Initiatives
To foster lasting peace between Armenia and Azerbaijan, initiatives must prioritize inclusivity and community engagement. Emphasizing the involvement of grassroots organizations and local leaders can bridge gaps and build trust between both nations. Key strategies include:
- Dialogue facilitation: Organizing platforms for open discussions among affected communities to share narratives and foster understanding.
- Joint cultural programs: Promoting collaborative art and cultural exchanges to celebrate shared heritage while respecting differences.
- Economic cooperation: Encouraging joint economic projects that provide mutual benefits and create interdependence.
| initiative Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Educational Workshops | Programs aiming to teach conflict resolution skills and peace studies in schools. |
| Habitat Projects | Collaborative efforts focused on shared environmental concerns to enhance regional cooperation. |
| Sports diplomacy | Joint sporting events that allow youth from both countries to compete and interact in a positive environment. |
Effective peacebuilding must also include international support aimed at developing systematic frameworks.This can be achieved thru:
- Monitoring mechanisms: Establishing neutral commissions to oversee dialogue progress and conflict resolution efforts.
- Resource allocation: Securing funding from international donors to support educational and community-building initiatives.
- Policy alignment: Encouraging alignment of local policies with international peace standards to ensure consistency and sustainability.
Future Prospects for Relations Between Armenia and Azerbaijan

as both countries navigate their turbulent history, the future of Armenia and Azerbaijan’s relations hinges on several critical factors. International mediation will play a pivotal role in facilitating dialogue, with organizations such as the OSCE Minsk Group and the European Union at the forefront. Their involvement may help bridge longstanding divides and promote confidence-building measures that foster trust between the two nations. additionally, addressing key issues such as territorial disputes, refugees, and economic cooperation is essential for creating a sustainable peace framework.
Moreover, public sentiment and grassroots movements will significantly influence diplomatic efforts. Both societies bear scars from conflict, which can lead to entrenched positions. Therefore, initiating cultural exchange programs and educational initiatives could aid in softening a hardened narrative. Furthermore,the role of regional powers,especially Turkey and Russia,cannot be overlooked as they have interests that may align or conflict with peace efforts. Thus, any future agreements will likely need to navigate a complex web of local aspirations and geopolitical strategies.
to Conclude
the ongoing tensions between Armenia and Azerbaijan serve as a poignant reminder of the complexities underlying peace processes in post-soviet states. Despite international efforts and diplomatic interventions aimed at fostering reconciliation, deep-seated historical grievances and nationalistic fervor continue to hinder progress. The Jamestown Foundation underscores that a sustainable resolution to the disputes over Nagorno-Karabakh and border issues will require not only robust negotiation frameworks but also a commitment to addressing the socio-political realities on the ground.as both nations stand at a critical juncture, the path forward demands patience, understanding, and a genuine willingness to forge a new narrative that prioritizes coexistence over conflict. The stakes are high, and the potential for both nations to achieve lasting peace remains uncertain. The international community must remain engaged, supporting initiatives that encourage dialogue and mutual respect between Armenia and Azerbaijan. Only through these efforts can the hope for a stable and prosperous future for the region be realized.