In a significant move towards preserving biodiversity in the Eastern himalayas, India and bhutan are set to launch a comprehensive conservation action plan aimed at safeguarding the endangered golden langur, a species endemic to the region.This initiative, reported by Deccan Herald, comes in response to mounting concerns over habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict, which have placed this charismatic primate at risk of extinction. The collaborative efforts between Indian and Bhutanese authorities reflect a growing recognition of the need for transboundary conservation strategies, as well as a commitment to protecting not only the golden langur but also the rich ecosystems they inhabit. The upcoming plan promises to address critical challenges faced by these unique primates while fostering sustainable coexistence between local communities and wildlife. Through expert-driven research, community engagement, and policy reform, the Indo-Bhutan conservation action plan aims to create a sustainable future for the golden langur and the natural heritage of the Himalayan region.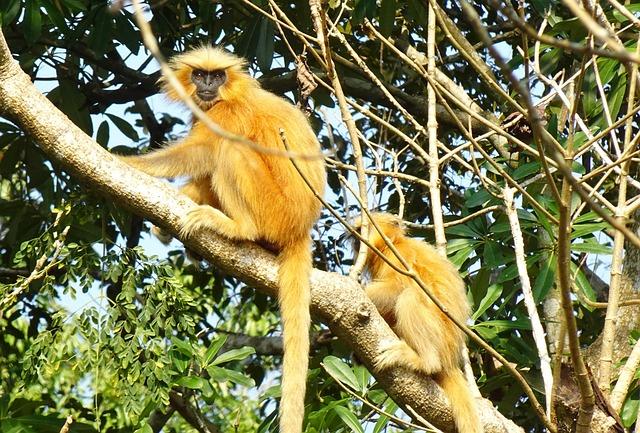
indo-Bhutan Collaboration: A Unified Approach to Golden Langur Conservation
the collaboration between India and Bhutan represents a significant milestone in the efforts to protect the endangered golden langur,a species endemic to the region. This partnership embodies a unified approach by combining resources, expertise, and conservation strategies from both nations. Key aspects of the plan include:
- Joint Research initiatives: Conducting comprehensive studies on golden langur behavior, habitat requirements, and population dynamics.
- Shared Monitoring Efforts: Implementing a coordinated system for monitoring golden langur populations across the border, ensuring a holistic understanding of their environmental needs.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts to foster stewardship and sustainable practices that benefit both the ecosystem and livelihoods.
As part of this ambitious action plan, both governments are investing in habitat restoration and protection measures aimed at creating a safer habitat for golden langurs. An important focus will be on resolving human-wildlife conflict, which poses a significant threat to their survival. The action plan will also include:
| Action Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Habitat Preservation | Identifying and preserving critical golden langur habitats through protected areas. |
| Awareness Programs | launching educational campaigns to inform the public about the importance of golden langurs. |
| Research Funding | Allocating resources for scientific research to better understand and protect the species. |
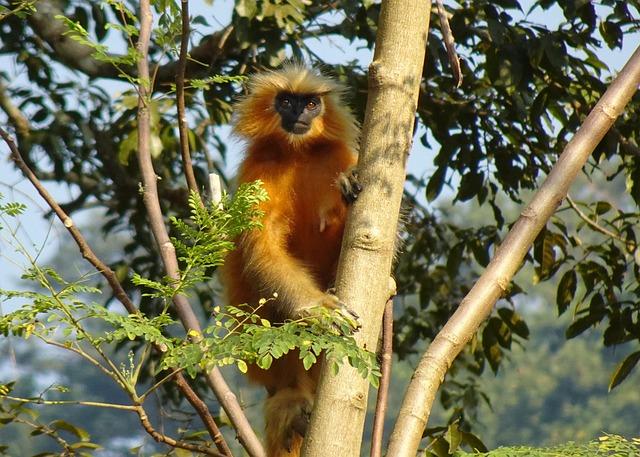

Crisis and Opportunity: Understanding the Threats Facing Golden Langurs
The golden langur, a species endemic to the region, faces numerous threats that jeopardize its survival. Habitat loss due to deforestation and agricultural expansion has dramatically reduced their natural habitat, pushing these primates into shrinking and fragmented areas.Pollution and human-wildlife conflict also pose significant risks, as increasing encroachment on their territory leads to encounters that frequently enough end negatively for the langurs. Additionally, climate change threatens their food sources and living conditions, amplifying the challenges they face in an already precarious environment.
Despite these alarming threats, there is a burgeoning opportunity for the conservation of golden langurs through collaborative efforts between India and Bhutan. The upcoming conservation action plan emphasizes restoration, protection, and community engagement as key strategies. By fostering local participation and awareness, this initiative aims to create a sustainable balance between human advancement and wildlife conservation. Collaborative efforts will include:
- Reforestation initiatives to restore habitat
- community education programs to promote coexistence
- Research and monitoring to better understand golden langur populations
| Threats | Opportunities |
|---|---|
| Deforestation | Reforestation initiatives |
| Human-wildlife conflict | Community education programs |
| Climate change | Research and monitoring |
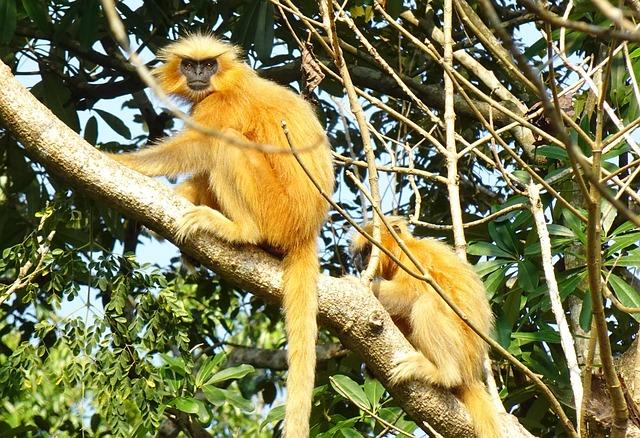

Key strategies in the Action Plan: Habitat Preservation and Community Engagement
To effectively safeguard the habitat of the golden langurs, the conservation action plan emphasizes proactive measures aimed at habitat preservation. Key strategies include:
- Protected Area Management: Establishing and expanding protected areas to ensure a safe environment for the golden langurs.
- Reforestation Initiatives: Implementation of reforestation efforts to regenerate the natural habitat and promote biodiversity.
- Wildlife Corridors: Creating wildlife corridors to facilitate movement and genetic interchange among langur populations.
In parallel, community engagement is vital to the success of these conservation efforts. local communities will be involved through various initiatives that promote awareness and participation. These initiatives may include:
- Educational Campaigns: Engaging local schools and organizations to raise awareness about the golden langurs and the importance of their conservation.
- Sustainable Livelihood Programs: Encouraging choice livelihoods that do not threaten the habitat and promote ecotourism.
- Participatory Monitoring: Involving local communities in monitoring golden langur populations and their habitats to foster a sense of ownership and responsibility.

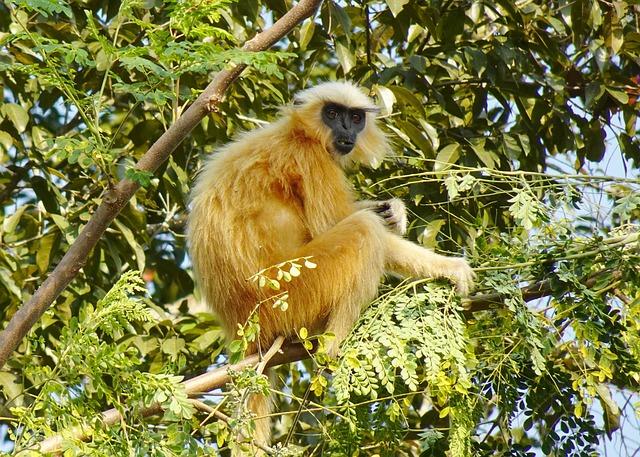
Role of Local Communities in Conservation Efforts for Golden Langurs
Local communities play a pivotal role in the conservation of golden langurs, a species unique to the Himalayan foothills that straddle India and Bhutan. By actively participating in conservation initiatives,these communities help protect the natural habitat of the langurs while also fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility towards their environment. Key contributions from local populations include:
- Monitoring Populations: Local residents often serve as the eyes and ears of conservation efforts, reporting sightings and health of the langur populations.
- Awareness Campaigns: Community-driven educational programs raise awareness about the importance of preserving the golden langurs and their habitats.
- sustainable Practices: By adopting eco-amiable agricultural and forestry practices, locals can mitigate habitat loss caused by deforestation and land conversion.
The collaboration between conservation organizations and local communities has led to innovative programs that emphasize coexistence between humans and wildlife. Workshops and training programs empower locals with skills to engage in responsible tourism, which not only generates income but also enhances commitment to conservation. as detailed below, some of the successful outcomes witnessed through this community involvement include:
| Outcomes | Description |
|---|---|
| increase in Langur Sightings | Regular monitoring has led to a noticeable rise in golden langur populations. |
| Community Engagement | Higher participation in conservation activities and decision-making processes. |
| Improved Livelihoods | Jobs created through eco-tourism initiatives, benefiting local economies. |

Evaluating Success: Monitoring and Measurement of Conservation Impact
Measuring the effectiveness of conservation efforts is critical to ensuring the long-term survival of the golden langurs in the indo-Bhutan region. The success of the recent conservation action plan will rely on a comprehensive monitoring strategy that includes both qualitative and quantitative metrics. These metrics may include:
- Population Dynamics: Regular surveys to estimate the size and growth rates of golden langur populations.
- Habitat Assessment: Evaluating habitat quality and identifying key areas needing protection or restoration.
- Community Engagement: Monitoring local community involvement and support for conservation initiatives.
To facilitate ongoing evaluation, a structured framework using indicators for success will be established. This framework will encompass:
| Indicator | Definition | Frequency of Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Langur Sightings | Number of golden langurs observed during field surveys. | Biannually |
| Forest Cover | Percentage of forested area within the langur’s habitat. | Annually |
| Community Surveys | Feedback from local residents regarding their attitudes towards conservation. | Every 2 years |

The Path Forward: Sustaining Interest and Funding for Long-term Protection
To ensure the longevity of the Indo-Bhutan conservation action plan for golden langurs, it is crucial to cultivate ongoing interest and secure sustainable funding. A multi-faceted strategy that includes collaboration between governments, NGOs, and local communities is vital. This coordinated approach should emphasize:
- awareness Campaigns: educating the public about the ecological importance of golden langurs and their habitat.
- Community Engagement: Involving local populations in conservation efforts to create a vested interest in protecting these species.
- Research Initiatives: Funding studies that assess population health and habitat conditions to inform future strategies.
Moreover, leveraging digital technology and social media can amplify conservation messages and drive funding initiatives. establishing partnerships with eco-conscious businesses and international organizations can also augment financial resources. A focused approach could include:
| Action Item | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Host Annual Conservation Forums | Increase visibility of conservation challenges and successes. |
| Create Crowdfunding Platforms | Mobilize resources for specific conservation projects. |
| Develop Educational Programs | Equip future generations with knowledge and tools for wildlife protection. |
Key Takeaways
the Indo-Bhutan conservation action plan represents a pivotal step in the collaborative effort to safeguard the golden langur, a species emblematic of the unique biodiversity found in the region. With initiatives rooted in habitat preservation, community engagement, and scientific research, this strategy promises to enhance the conservation landscape for the golden langur while fostering sustainable development in local communities. As stakeholders from both countries come together to implement this plan, the hope is not only for the survival of the golden langur but for the broader ecosystem it inhabits. The commitment to such cross-border initiatives underscores the importance of cooperative conservation efforts in addressing the pressing environmental challenges faced by both nations. As we move forward, the success of this action plan may serve as a model for future collaborations aimed at preserving our planet’s rich natural heritage.