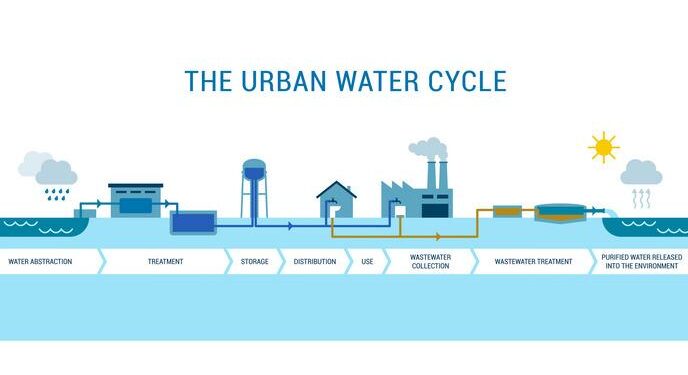
In the face of escalating climate challenges, securing reliable urban water supplies has become a critical concern-especially in tropical regions where heat and rainfall patterns are increasingly unpredictable. A new study published in Nature sheds light on the complex risks urban centers face under tropical climatic conditions, offering a comprehensive assessment that could reshape how cities prepare for water scarcity and flooding. As populations surge and infrastructure strains under environmental pressures, this timely research underscores the urgent need for adaptive strategies to safeguard the lifeblood of tropical metropolises: their water supply.
Assessing Urban Water Supply Challenges in Tropical Climates
Rapid urbanization in tropical regions intensifies pressure on existing water infrastructure, exacerbating the risks of supply disruptions. High temperatures combined with erratic rainfall patterns contribute to frequent droughts and severe flooding, both of which undermine water quality and availability. Infrastructure degradation, compounded by limited investment in maintenance, leaves cities vulnerable to contamination and leakage. Further complicating the scenario, rising population densities increase demand, stretching resources thin and amplifying inequities in access among different urban communities.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted strategy that prioritizes resilience and sustainability. Key areas of focus include:
- Enhanced data monitoring: Real-time hydrological and climate data improve prediction capabilities for extreme weather events.
- Innovative infrastructure: Integration of green infrastructure such as rain gardens and permeable pavements can bolster groundwater recharge.
- Decentralized water systems: Local treatment and reuse reduce dependence on centralized supply and increase flexibility.
- Community engagement: Participatory water management ensures equitable distribution and promotes conservation behaviors.
| Challenge | Impact | Mitigation Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Seasonal droughts | Water scarcity, increased conflict | Rainwater harvesting |
| Flooding | Infrastructure damage, contamination | Stormwater management |
| Population growth | Demand outpaces supply | Decentralized treatment |
Understanding Climate-Driven Risks to Urban Water Infrastructure
Urban water infrastructure in tropical regions faces increasing uncertainty due to the escalating impacts of climate variability and extreme weather events. The combined effect of intense rainfall, extended droughts, and rising temperatures is impairing the reliability of water supply systems, leading to heightened vulnerability of urban populations. Critical components such as reservoir capacity, distribution networks, and wastewater treatment plants are frequently challenged by fluctuating water availability and quality, demanding adaptive strategies that move beyond traditional engineering solutions.
Key factors contributing to the vulnerability of urban water infrastructure include:
- Unpredictable precipitation patterns: Leading to both flooding risks and scarcity periods.
- Increased water demand: Driven by rapid urbanization and population growth.
- Infrastructure aging: Exacerbating system fragility under stress conditions.
- Saltwater intrusion: Particularly in coastal cities, threatening freshwater supplies.
| Climate Stressor | Impact on Infrastructure | Potential Adaptive Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Rainfall | Flooded pumping stations | Elevate infrastructure, enhance drainage |
| Prolonged Drought | Reservoir depletion | Implement water reuse and conservation |
| Heat Waves | Increased pipe bursts | Upgrade materials, monitor temperatures |
Strategic Recommendations for Enhancing Water Security in Tropical Cities
Prioritizing integrated water management approaches is essential for tropical cities facing escalating climate-related pressures. Urban planners and policymakers must adopt systems that simultaneously address water supply, demand management, and ecosystem protection. Enhancing green infrastructure-such as urban wetlands and permeable surfaces-not only mitigates flood risks but also replenishes groundwater reserves, creating resilient water cycles. Additionally, decentralized water treatment and reuse solutions offer scalability and reduce dependency on single-source supplies, vital under unpredictable rainfall patterns.
Investment in advanced monitoring and data analytics can transform water governance frameworks. Implementing real-time sensor networks enables early detection of supply disruptions and contamination, allowing swift response to protect public health. Furthermore, fostering community engagement through public education campaigns promotes water conservation behaviors critical for sustainability. Below is a summary of recommended strategic actions:
- Enhance green infrastructure to improve natural water retention and filtration.
- Implement decentralized wastewater treatment for reuse and reduced pressure on central systems.
- Deploy real-time monitoring to anticipate and mitigate supply risks.
- Encourage community participation in water-saving initiatives.
| Strategy | Key Benefit | Primary Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Green Infrastructure | Flood mitigation & groundwater recharge | Land availability and urban planning |
| Decentralized Treatment | Local water reuse & supply diversity | Infrastructure costs and management |
| Real-time Monitoring | Early risk detection | Technology adoption & data integration |
| Community Engagement | Behavioral change to reduce demand | Public awareness and sustained participation |
The Way Forward
As urban centers in tropical regions continue to expand, understanding the risks to water supply systems has never been more crucial. This in-depth assessment highlights the complex challenges posed by climate variability, population growth, and infrastructure vulnerabilities. Addressing these risks requires coordinated efforts between policymakers, engineers, and communities to build resilient, sustainable water networks. As cities grapple with the realities of a changing climate, such research underscores the urgent need to safeguard one of humanity’s most vital resources.