in a bid to counteract the economic impacts of ongoing trade tensions, particularly the tariffs imposed by the United States during Donald Trump’s presidency, China has unveiled a thorough plan aimed at boosting domestic consumption. The initiative comes as Chinese economists and policymakers seek to insulate the world’s second-largest economy from external shocks and strengthen its internal market. With the trade war casting a long shadow over its export-driven growth model, China is pivoting toward a consumption-led strategy that promises to reshape the landscape of its economy. This article explores the key elements of China’s plan, the challenges it faces, and the implications for both domestic businesses and global trade relations.
China’s Strategic Response to Tariffs Through Increased Domestic Consumption

in the wake of increased tariffs imposed by the United States, China is strategically pivoting towards enhancing domestic consumption as a buffer against external economic pressures. This move is not merely reactive; it represents a long-term vision for sustainable growth that minimizes reliance on exports. The Chinese government has outlined several key initiatives aimed at rejuvenating the consumption landscape, including:
- incentives for Consumer Spending: Financial subsidies and tax breaks aimed at middle-class families to encourage purchases of goods ranging from electronics to household items.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Continued investment in transportation and logistics to facilitate easier access to products and services for consumers across the country.
- Support for Local Brands: Government campaigns promoting domestic brands to encourage shoppers to support home-grown enterprises.
To give a clearer picture of the expected growth in domestic consumption,a recent analysis presents growth projections for key sectors poised to benefit from this initiative:
| Sector | Current Growth Rate (%) | Projected Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | 8.5 | 10.2 |
| Technology | 7.2 | 9.0 |
| Automotive | 5.0 | 7.5 |
| Health & Wellness | 6.8 | 9.7 |
This focus on bolstering consumption not only aims to sustain economic growth amidst global trade tensions but also seeks to empower the Chinese consumer,fostering a sense of stability and confidence in the domestic economy. As these strategies unfold, their effectiveness in mitigating the impacts of tariffs will be pivotal for China’s future economic landscape.
Key Sectors Targeted for growth: Retail,Automotive,and Technology

As part of its strategic approach to enhance domestic consumption amid external pressures, China is honing in on three pivotal sectors: Retail, Automotive, and Technology. The retail landscape is anticipated to undergo change, targeting increased sales through enhanced online platforms and unique shopping experiences. This will not only stimulate local demand but also position chinese brands to compete more aggressively both domestically and globally. Key initiatives include:
- Expansion of e-commerce platforms to bolster connectivity between producers and consumers.
- Promotional campaigns tailored to boost spending during major shopping festivals.
- Support for small and medium enterprises to innovate and diversify their offerings.
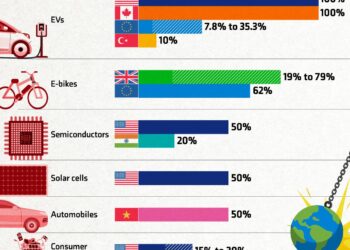
The automotive sector, recognized as a cornerstone of economic growth, is set to benefit from measures aiming to increase the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technology. With the push for greener alternatives, a meaningful influx of investment will be funneled into R&D and infrastructure growth. Focus areas include:
| Initiative | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Subsidies for EV Purchases | Financial incentives for consumers to buy electric vehicles. | Increased EV sales and reduced carbon emissions. |
| Charging Infrastructure expansion | Investment in charging stations across urban and rural areas. | Enhanced accessibility and convenience for EV users. |
| Autonomous Driving Research | Funding for the development of AI-driven vehicles. | Position China as a leader in automotive technology. |
Lastly, the technology sector remains a focal point, as innovation will be key to drive consumption in a rapidly digitizing economy. The government’s backing for homegrown tech firms aims to not only reduce reliance on foreign technology but also foster an ecosystem conducive to growth and sustainability. Key strategies involve:
- Incentives for startups developing artificial intelligence, big data, and cloud computing solutions.
- Investment in digital infrastructure to enhance connectivity across urban and rural landscapes.
- Collaboration with educational institutions to nurture a tech-savvy workforce equipped for future challenges.
Consumer Confidence Boosters: Incentives and Policy Changes

In response to the growing economic uncertainties stemming from escalating trade tensions, the Chinese government has introduced a series of strategic initiatives aimed at enhancing consumer confidence and stimulating domestic consumption. Among these efforts are tax incentives and subsidies designed to encourage spending among households. The government is prioritizing sectors such as technology, automotive, and retail to promote sustainable growth.These measures include:
- Tax relief on consumer electronic purchases to incentivize upgrades.
- Cash rebates for vehicles, especially electric models, to bolster the auto industry.
- Enhanced support for small businesses through grants that aid in marketing and service expansion.
Additionally, policy changes are being enacted to improve the overall economic landscape. By easing regulations on e-commerce and expanding digital payment systems, the government aims to create a more fluid marketplace that empowers consumers. The latest initiatives also encompass:
| Policy Measure | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Lower VAT rates | To reduce prices for consumers across various goods. |
| Investment in infrastructure | To enhance supply chains and accessibility for consumers. |
| Public awareness campaigns | To promote confidence in local products and services. |
Long-term Economic Implications of Consumption-Focused Strategies

The Chinese government’s strategy to stimulate domestic consumption in response to external economic pressures signals significant long-term consequences for its economy. By prioritizing consumer spending, China aims to shift its economic focus from exports to a more balanced model that relies heavily on domestic demand. This could potentially mitigate the adverse effects of tariffs imposed by the United States and other trade partners, as a robust internal market woudl cushion the economy from external shocks. Over time, this transformation holds the promise of fostering a new wave of innovation and entrepreneurship, as local businesses adapt to the evolving preferences of an increasingly affluent consumer base.
However, the sustainability of such consumption-oriented strategies depends on several critical factors:
- Income Distribution: Ensuring that income growth reaches all segments of society is imperative for fostering a consumer-driven economy.
- Consumer Confidence: Economic policies must inspire confidence among consumers,encouraging them to increase spending and investment.
- Environmental concerns: Balancing consumption growth with environmental sustainability will be crucial in maintaining economic stability.
To illustrate the potential outcomes, the following table outlines various economic indicators that may be influenced by a shift toward consumption-driven growth:
| Indicator | short-term Effect | Long-term Effect |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth | Moderate increase due to heightened consumer spending | Potential for sustained growth if supported by innovation |
| Employment Rates | Incremental job creation in retail and services | Improved job stability and opportunities across sectors |
| Inflation | Possible uptick as demand rises | Need for careful monitoring to avoid overheating |
International Reactions and the Future of China-U.S. Trade Relations

As the global community closely watches the unfolding situation between China and the United States, international responses to China’s initiatives to bolster domestic consumption reflect a keen interest in the implications for future trade relations. Several countries, particularly those in the Asia-Pacific region, have expressed both concern and chance as they consider the ripple effects of shifting trade dynamics. Key reactions have included:
- Regional Trade Partners: Countries like Japan and South Korea are wary of the potential impact on their own exports to China, prompting discussions on diversifying supply chains.
- Western Allies: European nations view china’s consumer-driven strategy as a way to stabilize the region’s economy, yet they remain cautious about the overarching implications of U.S.-China tensions.
- Emerging Markets: Nations in Southeast Asia see this as an opportunity to strengthen trade relations with China by positioning themselves as alternatives to U.S. goods.
Looking forward, the trajectory of China-U.S. trade relations will likely hinge on how effectively both parties navigate the challenges posed by tariffs and geopolitical tensions. The current atmosphere necessitates a balance between protectionist measures and cooperative initiatives, emphasizing mutual economic interests. The following table summarizes projected areas of impact on trade relations:
| Area of Impact | China’s Strategy | Potential Response from U.S. |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Goods | Boosting local production | Re-evaluating tariff policies |
| Technology Sector | Investing in R&D | Increased scrutiny on tech imports |
| Agricultural Exports | Expanding imports from other nations | Potential retaliatory tariffs |
Sustainable Practices in Consumption Growth: Balancing Economy and Environment

In response to the ongoing challenges posed by external economic pressures, china is exploring ways to enhance domestic consumption while embracing sustainable practices. The government aims to create an intricate balance between economic growth and environmental stewardship. One facet of this approach involves incentivizing businesses to adopt eco-friendly production processes, which not only streamline operations but also cater to a growing consumer preference for sustainability.
To facilitate this shift, policies are being rolled out that encourage green technologies and support sustainable consumer goods.These initiatives include:
- Tax breaks for companies that invest in clean energy.
- Funding for research into sustainable materials.
- Public awareness campaigns to promote greener choices.
Moreover, consumer education plays a pivotal role in this transition. By informing the public about the benefits of purchasing sustainably produced goods, China hopes to stimulate demand for products that are both economically beneficial and environmentally responsible. The strategy not only tackles immediate economic concerns but also positions China as a global leader in sustainability, ultimately contributing to a more resilient and balanced economy.
In Summary
China’s comprehensive strategy to enhance domestic consumption emerges as a pivotal response to the challenges posed by ongoing tariffs imposed by the United States under the Trump administration. By focusing on boosting consumer spending and fostering a more resilient economic landscape, Beijing aims to mitigate the impact of trade tensions and ensure sustainable growth.As the government invests in initiatives to stimulate demand and improve consumer confidence, the effectiveness of these measures will be critical not only for China’s economic trajectory but also for the broader dynamics of international trade.Observers will be closely watching how these developments unfold,as the interplay between consumption and tariff policy continues to shape the global economic landscape.