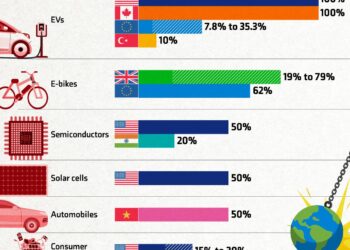
As one of the world’s largest economies and an influential global power, China plays a pivotal role in shaping international relations. The United States, recognizing this significance, has maintained a complex and multifaceted relationship with China characterized by cooperation, competition, and conflict. The U.S. Department of State serves as the primary channel through which American foreign policy engages with this crucial nation, navigating the delicate balance between promoting diplomatic dialog and addressing the challenges that arise in areas such as trade, human rights, and security. this article delves into the evolving dynamics of U.S.-China relations as framed by the Department of State, analyzing key policies, recent developments, and the implications for both nations and the broader international community. As tensions rise and alliances shift, understanding this relationship is essential for grasping the future of global politics.
U.S. Strategic Interests in China: Balancing Engagement and Competition
In navigating the complexities of U.S.-China relations, American policymakers are tasked with a dual mandate: fostering engagement while together addressing the competitive elements of this crucial bilateral relationship. The U.S. recognizes that China plays a vital role in global economic dynamics, making cooperation essential in areas such as trade, climate change, and public health. Key areas for engagement include:
- Trade and Investment: Promoting fair trade practices and addressing tariffs.
- Climate Change: Collaborating on environmental initiatives and sustainable energy solutions.
- Public Health: Coordinating efforts to combat pandemics and share research.
However, the competitive aspects of the relationship cannot be overlooked. U.S. interests are increasingly challenged by China’s assertive policies in the Asia-Pacific region, as well as its military expansion and technological advancements. To safeguard national security and uphold the rules-based international order, the U.S. is strategically enhancing its partnerships with allies in the region. Critical strategies include:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Strengthening Alliances | Enhancing military and diplomatic ties with regional partners. |
| Technological Innovation | Investing in R&D to maintain a competitive edge in key technologies. |
| Economic Resilience | Diversifying supply chains to reduce dependence on chinese manufacturing. |

Human Rights and Ethical Leadership: U.S. Principles in Diplomatic Dialogues
In the context of U.S.-China relations, the integration of human rights and ethical leadership remains a pivotal theme in diplomatic dialogues. The U.S. government emphasizes the importance of safeguarding essential freedoms and promoting democratic values, notably as these principles resonate with the broader global community. Through strategic conversations, U.S. officials prioritize key issues such as:
- Freedom of Expression: Advocating for the protection of free speech and media independence in China.
- Religious Liberty: Highlighting the need for respect toward religious beliefs and practices.
- Minority Rights: Addressing the treatment of ethnic minorities and advocating for equitable policies.
- Rule of Law: Encouraging adherence to international norms and regulations.
To illustrate the goals of U.S. ethical leadership, the following table summarizes critical engagement strategies employed in diplomatic efforts:
| Strategy | Objective | Current Status |
|---|---|---|
| High-Level Dialogues | Foster mutual understanding on human rights | Ongoing |
| Public Statements | Raise awareness of rights violations | regular |
| Bilateral cooperation | Enhance collaborative projects | In Growth |
| Multilateral Engagements | Leverage global platforms for advocacy | Active |

Trade Relations and Economic Policies: Navigating Complex Interdependencies
Trade relations between the U.S. and China represent a labyrinth of mutual interests and strategic maneuvers. The intertwining of economic policies has led to meaningful dependencies that both nations navigate daily. key factors influencing this relationship include:
- Tariffs and Trade Barriers: Ongoing tariffs have reshaped supply chains, impacting costs and consumer prices.
- Currency Manipulation: Concerns over currency policies have driven discussions on economic fairness and stability.
- Technology Transfer Regulations: Policies governing technology sharing are crucial for safeguarding national interests while facilitating innovation.
Diplomatic engagements often reflect these complexities, as both countries seek to balance competitive interests with necessary cooperation. Recent dialogues involve discussions on:
| Discussion Theme | Current Status | Future Prospects |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Change Cooperation | Outreach efforts initiated | Potential for joint initiatives |
| Supply Chain Resilience | Ongoing reviews | Strategic alliances expected |
| Intellectual Property Rights | Negotiations in progress | Increased protection anticipated |

Climate Change Cooperation: Opportunities for Collaborative Solutions
Climate change represents one of the most pressing global challenges, and cooperation between the U.S. and China is essential to address its impacts effectively.Both nations,being the largest emitters of greenhouse gases,can leverage their technological advancements and resources to pioneer effective solutions. Collaborative projects could focus on:
- Joint renewable energy initiatives: Investing in solar, wind, and other choice energy sources.
- Carbon capture technologies: sharing research and development resources for innovative carbon mitigation strategies.
- Climate adaptation frameworks: Developing strategies to enhance resilience against climate-induced hazards.
Engaging in dialogue and partnerships opens avenues for both nations to share expertise, funding, and innovation. A cooperative framework could enable the establishment of a bilateral task force that monitors progress and identifies opportunities for further engagement.Consider the following potential mechanisms for collaboration:
| Collaboration Areas | Possible Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Technology exchange | Enhanced capacity to implement green technologies |
| Policy Alignment | Shared regulatory standards for emissions |
| Public Awareness Campaigns | Increased engagement and education on climate issues |

regional Security Dynamics: Addressing North Korea and South China Sea Tensions
The evolving security dynamics in East Asia are significantly shaped by the dual challenges posed by North Korea’s nuclear ambitions and the ongoing tensions in the south China Sea. North Korea remains a critical concern for the United States and its allies, navigating a landscape filled with provocative missile tests and nuclear development.Engaging in a thorough strategy that combines diplomacy and deterrence is essential to mitigate the risks of further escalation. Strengthening alliances with South Korea and Japan and enhancing military readiness in the region serves as a deterrent while enabling active dialogue with North Korea to pursue denuclearization and peace on the Korean Peninsula.
Concurrently, the situation in the South China Sea highlights the need for robust responses to China’s assertive territorial claims.The U.S.supports freedom of navigation and overflight rights, actively conducting maritime operations to demonstrate commitment to international laws and norms. Strategic partnerships with ASEAN nations and engagement in trilateral dialogues are pivotal in maintaining a united front against destabilizing actions. A multi-faceted approach that incorporates economic cooperation,diplomatic channels,and security assurances can definately help ensure stability in this critical maritime zone.

Future Directions: Recommendations for strengthening U.S.-China Relations
Strengthening U.S.-china relations requires a multifaceted approach that encourages dialogue, fosters cooperation, and addresses underlying tensions. To achieve this, key stakeholders should prioritize open communication channels at all levels, from government officials to local communities. This can be facilitated through:
- Regular bilateral summits focusing on economic cooperation and security issues.
- Enhanced cultural and educational exchanges to promote mutual understanding.
- Joint initiatives addressing climate change, which can act as a unifying issue.
Additionally, implementing a strategic framework for economic engagement is essential to mitigate trade tensions. As part of this framework, both countries should establish clarity measures that promote fair market practices. This could include:
| Measure | Impact |
|---|---|
| Regular trade dialogue meetings | Address tariffs and trade barriers |
| Collaborative research projects | Advance technology and innovation |
| Investment in sustainable industries | Boost green technology cooperation |
incorporating these strategies will not only alleviate immediate conflicts but also build a framework for long-term cooperation that reflects the interconnected nature of both nations in the global landscape.

The Conclusion
the dynamics of U.S.-China relations remain one of the most critical geopolitical issues of our time.The Department of State continues to navigate a complex landscape characterized by cooperation, competition, and confrontation. As the two nations grapple with a myriad of challenges—from trade disputes and technological advancements to climate change and human rights concerns—it is evident that a balanced approach will be essential for fostering a sustainable relationship. The intricacies of these interactions not only affect the two countries but also reverberate across the globe, influencing international alliances and economic policies. As we look ahead, the importance of diplomacy, open communication, and mutual understanding cannot be overstated. The path forward will require both nations to engage thoughtfully, with a commitment to dialogue and respect for each other’s perspectives, paving the way for a more stable and productive future in their bilateral ties.