In a significant policy shift aimed at bolstering its pharmaceutical sovereignty, the European Union has unveiled ambitious plans to reduce its dependence on Asian manufacturing for essential antibiotics and other critical medications. As global supply chains have been increasingly strained, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, the EU’s initiative reflects growing concerns over the security and reliability of drug supply in the face of geopolitical tensions and public health emergencies. The announcement, reported by Reuters, underscores the bloc’s commitment to ensuring that its healthcare systems are resilient, with a focus on fostering local production capabilities while mitigating potential shortages that could arise from foreign dependencies. This strategic move comes as part of a broader effort to enhance drug safety, safeguard public health, and stimulate innovation within the European pharmaceutical industry.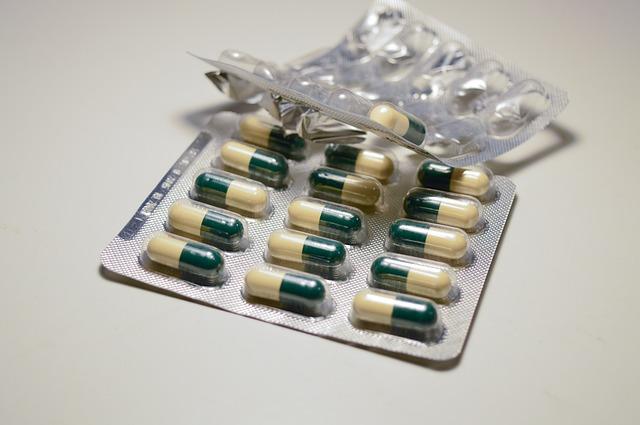
EU’s Strategic Shift: reducing Dependency on Asian Pharmaceuticals
Amid growing concerns over supply chain vulnerabilities, the European Union has initiated a comprehensive strategy aimed at decreasing its dependency on Asian pharmaceutical manufacturing, particularly for antibiotics and other essential medications. This strategic shift arises from disruptions experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic, revealing the fragility of relying heavily on foreign production.Officials emphasize the importance of cultivating a more robust, self-sufficient drug supply chain within Europe, focusing on enhancing domestic production capabilities and ensuring a steady flow of critical medical supplies.
The EU’s plan includes several key initiatives designed to bolster local pharmaceutical industries:
- Investment Incentives: Providing financial support to companies willing to relocate their production to EU member states.
- Research and Progress: Encouraging innovation in pharmaceuticals by funding new technologies and processes.
- Collaborations: Establishing partnerships between public institutions and private enterprises to strengthen supply chains.
- Regulatory Reforms: Streamlining approval processes for local manufacturing to facilitate quicker ramp-up times.
| Key Initiative | Objective |
|---|---|
| investment Incentives | Boost local production |
| Research and Development | Drive innovation |
| Collaborations | Strengthen industry ties |
| Regulatory Reforms | Facilitate faster approvals |

Understanding the Risks: The Susceptibility of Europe’s Drug Supply chain
The recent EU initiative to reduce its dependence on Asian suppliers for critical drugs, including antibiotics, highlights the inherent vulnerabilities within Europe’s pharmaceutical supply chain. Over the years, a significant proportion of essential medications has been sourced from just a handful of countries, primarily in Asia, raising alarms about resilience and supply chain stability.Factors such as geopolitical tensions, trade restrictions, and the COVID-19 pandemic have illustrated just how quickly reliable access to medications can be jeopardized, leaving patients and healthcare systems vulnerable. The consequences can be dire, particularly for those requiring timely access to lifesaving treatments.
To better understand the risks, it is essential to consider various aspects of the supply chain:
- Concentration of Production: A large share of antibiotics and critical medicines is produced in a few countries, presenting a single point of failure.
- regulatory Challenges: different regulatory environments may hinder swift adaptation and response to issues impacting supply.
- Quality control Issues: Variability in manufacturing standards can lead to quality and safety concerns.
Moreover, in light of these vulnerabilities, the EU’s plan includes incentivizing local production and encouraging diversified sourcing strategies. The table below outlines key goals of this initiative:
| Goal | Description |
|---|---|
| Increase Local Manufacturing | Support the establishment of pharmaceutical manufacturing plants within EU borders. |
| Diverse Sourcing | Encourage member states to source medications from multiple regions. |
| Strengthen Supply Chain Resilience | Implement risk assessments and develop contingency planning frameworks. |

Key Initiatives in the EU’s New Health Strategy for Antimicrobial Production
The EU has unveiled a roadmap to bolster its resilience against external vulnerabilities in the supply chain for crucial medications, particularly antibiotics.This initiative is aimed at enhancing self-sufficiency and minimizing dependence on Asia, where a significant portion of antibiotic production currently takes place. Among the core objectives are:
- Investment in Local Manufacturing: Increased funding for domestic pharmaceutical production facilities to stimulate local economies and ensure a robust supply chain.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Encouragement of collaborations between governments and pharmaceutical companies to foster innovation in drug manufacturing.
- Regulatory Reforms: Simplifying approval processes for new antibiotic production methods and reinforcing quality assurance standards.
- Research and Development Incentives: Financial incentives for companies engaged in developing novel antibiotics and alternative therapies.
To facilitate these ambitious changes, the EU is looking at the establishment of dedicated task forces to oversee the implementation of these initiatives and monitor progress.Furthermore,a transparent system for evaluating the performance of antibiotic suppliers will be put in place. The emphasis will also be placed on sustainability, with plans to incorporate environmentally-friendly practices into antibiotic production. The key metrics to be assessed include:
| Metric | Target |
|---|---|
| Increase in Local Production Capacity | 30% by 2030 |
| Reduction in Import Dependency | Max 50% by 2025 |
| Investment in R&D for New Antibiotics | €300 million annually |

Investment in Local manufacturing: A Path to Drug Security
The recent shift towards strengthening local drug manufacturing within the EU comes as a critical response to the over-dependence on Asian production for essential pharmaceuticals.This strategy aims to bolster national capabilities and ensure uninterrupted access to life-saving medications, particularly antibiotics.By investing in local facilities and fostering collaboration between governments, industry stakeholders, and research institutions, the EU seeks to mitigate supply chain vulnerabilities that have been laid bare by recent global health crises.
Key components of this investment strategy include:
- Enhanced Infrastructure: Upgrading existing manufacturing plants and establishing new facilities to meet global quality standards.
- Incentives for Innovation: Providing grants and subsidies to encourage the development of advanced manufacturing technologies.
- Skilled Workforce Development: Investing in training programs to equip the workforce with the necessary skills for modern pharmaceutical production.
To further illustrate these initiatives, the following table summarizes the projected milestones and outcomes of the EU’s investment in local drug manufacturing:
| Milestone | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Establishment of R&D Centers | Increased innovation and faster drug development processes. |
| Implementation of Sustainable Practices | Reduction of environmental impact and improved public health outcomes. |
| Partnerships with Local Universities | Enhanced knowledge transfer and workforce readiness. |

collaboration and Innovation: Engaging Stakeholders in Essential Drug Production
In a significant shift towards enhancing self-sufficiency in healthcare,the EU is prioritizing the involvement of various stakeholders to revitalize essential drug production. By fostering collaboration among pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and governmental bodies, the initiative aims to create a robust ecosystem that supports local manufacturing of antibiotics and other critical medications. This approach recognizes the need for diverse input and expertise to drive innovation and efficiency in drug development, ensuring that the supply chain is both reliable and responsive to public health needs.
Engaging stakeholders is crucial not just for production, but also for developing cutting-edge solutions to existing challenges. Key focus areas include:
- Research Partnerships: Collaborative projects aimed at discovering new antibiotics and improving existing formulations.
- Funding Initiatives: Establishing financial support to encourage startups and innovators in the pharmaceutical industry.
- Regulatory Harmonization: Streamlining processes across member states to expedite the approval of new drugs.
By leveraging the strengths of various stakeholders, the EU envisions a sustainable model of drug production that not only alleviates dependency on external sources but also drives breakthroughs that align with the evolving public health landscape.

Policy Recommendations for Sustainable Antibiotic Development in Europe
To ensure a robust and sustainable framework for antibiotic production in Europe, several critical measures must be implemented. Incentivizing innovation within the pharmaceutical sector can catalyze the development of new antibiotics. This can be achieved through grants, tax breaks, or public-private partnerships focused on research and development. Moreover, fostering collaboration among countries in the EU to share best practices and research findings can amplify efforts to combat antibiotic resistance. Investment in local manufacturing must also be prioritized to reduce dependency on external suppliers, thereby enhancing the security of drug supply chains.
Regulatory frameworks should be revised to streamline the approval process for new antibiotics, balancing the need for rigorous safety assessments with the urgency of public health requirements. A potential method to achieve this is by adopting adaptive licensing models that allow for phased approvals based on early-stage efficacy. Additionally, establishing a European Antibiotic Research Consortium can coordinate efforts across borders and sectors. It is also essential to engage stakeholders, including healthcare providers, researchers, and the public, to heighten awareness about the importance of judicious antibiotic use. Together, these initiatives can form a holistic strategy to strengthen Europe’s position in antibiotic development.

In Conclusion
the European Union’s recent announcement to reduce its dependency on Asia for antibiotics and other essential pharmaceuticals marks a significant step towards enhancing the region’s self-sufficiency and resilience in public health. By fostering domestic production and encouraging investment in local manufacturing, the EU aims to mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions, a concern that has been amplified by the COVID-19 pandemic. As policymakers work to implement these plans, the focus will be on balancing cost-effectiveness with the imperative of ensuring timely access to critical medications. The success of this initiative may not only redefine Europe’s pharmaceutical landscape but could also set a precedent for other regions grappling with similar challenges. As the situation evolves, stakeholders will need to closely monitor the impact of these strategic shifts on drug availability, safety, and innovation across the continent.