In a region often characterized by traditional values and conservative attitudes towards LGBTQ+ rights, Thailand is emerging as a surprising beacon of progress. The nation has taken significant strides toward legalizing same-sex marriage, positioning itself as a leader in Southeast Asia’s ongoing dialogue about LGBTQ+ equality. This shift not only reflects changing societal norms within Thailand but also presents a potential catalyst for broader reform across the region. As policymakers and advocates push for recognition and rights, Thailand’s developments could set a precedent for neighboring countries grappling with similar issues. This article explores how thailand is breaking the mold on same-sex marriage, the societal impacts of these changes, and the broader implications for LGBTQ+ rights in Southeast Asia.
Redefining Legal Norms: Thailand’s Path to Same-Sex Marriage Legislation
The trajectory toward same-sex marriage legislation in Thailand marks a significant shift in legal norms across Southeast Asia, an area traditionally known for its conservative values on marriage and family.As societal attitudes evolve, Thailand stands at the forefront, redefining legal frameworks to accommodate the rights of LGBTQ+ individuals. The Thai government has acknowledged the demand for equality, navigating public sentiment and lobbying efforts from advocacy groups. Key components of the legislative reform consider factors such as:
- Legal Recognition: Establishing legal groundwork for same-sex couples, including marriage licenses and family rights.
- Public Support: Increasing visibility and acceptance of LGBTQ+ issues within Thai society, demonstrated through pride events and media depiction.
- International Pressure: Drawing inspiration from global movements that advocate for human rights and equality, influencing domestic policies.
As the Thai parliament deliberates proposed bills, the potential impacts extend beyond judicial reform; they touch the lives of countless individuals seeking affirmation and recognition of their relationships. By fostering a legal surroundings that embraces diversity, Thailand not only stands as a beacon for LGBTQ+ rights in the region but also promotes broader discussions about personal freedoms and civil rights. A comparative overview of the current legal landscape in Southeast Asia reveals the following:
| country | Same-Sex Marriage Status | Recent Developments |
|---|---|---|
| Thailand | Pending Legislation | Government proposal for same-sex marriage in 2023 |
| Vietnam | non-Recognition | Legal yet unrecognized; no formal marriage |
| Malaysia | Illegal | Severe penalties for same-sex relationships |
| Philippines | Pending Legislation | Ongoing debates in Congress for civil unions |

Cultural Shifts and Public Support: The Changing Attitudes Towards LGBTQ+ Rights
as societal views on LGBTQ+ rights evolve, Thailand has emerged as a beacon in Southeast Asia, challenging traditional beliefs and encouraging a broader cultural acceptance. Over the past decade, public support for same-sex marriage has gained significant momentum, reflecting deep shifts in the collective consciousness. citizens are increasingly voicing their support through various platforms, including social media and public demonstrations, leading to a more open dialogue surrounding LGBTQ+ issues. This change is not solely attributed to advocacy groups but has been propelled by influential pop culture representations and the younger generation’s desire for equality and inclusivity.
The Thai government has begun to respond to this cultural shift, examining potential legislative frameworks that could legalize same-sex marriage.Various surveys indicate a growing acceptance among the populace, with many recognizing the importance of equal rights for same-sex couples. Some key factors contributing to this change include:
- Increased Visibility: Media representation has fostered greater awareness and empathy towards LGBTQ+ individuals.
- Youth Advocacy: Younger generations actively campaign for equality, driving public discourse.
- Global Influence: International progress on LGBTQ+ rights has inspired local movements.
As Thailand stands at the forefront of change in the region, its progressive attitude serves as a template for neighboring countries. the forthcoming legislation stands to reflect both public sentiment and a commitment to upholding human rights, perhaps reshaping the landscape of LGBTQ+ recognition across Southeast Asia. This pivotal moment might not only signify a change in policy but also a transformation in societal perceptions, illustrating how cultural shifts can catalyze progress in the quest for equality.

Comparative Analysis: Thailand’s Position in Southeast Asia’s Marriage Equality Landscape
Thailand’s approach to marriage equality distinctly sets it apart in Southeast Asia, where many neighboring countries still grapple with traditional views on LGBTQ+ rights. As of now, Thailand is at a crossroads, showcasing a unique blend of cultural acceptance and legislative progress. The social landscape here is more welcoming compared to regional counterparts,as evidence from various public opinion surveys suggests a significant percentage of Thais support same-sex marriage. key factors contributing to this shift include:
- Cultural Acceptance: A rich tapestry of buddhist influences that promote compassion and tolerance.
- Activism: A resilient LGBTQ+ community that has long advocated for rights and visibility.
- Government Initiatives: Ongoing discussions within the Thai parliament about legalizing same-sex marriage.
Despite these progressive tendencies, challenges remain, especially in the form of legislative hurdles and conservative pushback. In comparison to other Southeast Asian nations—many of which still have strict laws against homosexuality—Thailand stands as a beacon of potential change. As an example,recent initiatives indicate a willingness from the Thai government to revise existing laws and embrace inclusivity. The following table summarizes the marriage equality status of several countries in the region:
| Country | legal Status of Same-Sex Marriage |
|---|---|
| thailand | In progress – Draft legislation proposed |
| Malaysia | Illegal |
| Vietnam | Recognizes same-sex marriage but with limitations |
| Philippines | pending legislation for recognition |

Challenges Ahead: Navigating Legal and Social Hurdles for Same-Sex Couples
Despite Thailand’s progressive stance on same-sex marriage,numerous legal and social obstacles still loom large on the horizon. Couples seeking to legally solidify their partnerships may encounter challenges such as the lack of extensive anti-discrimination laws and an inadequate legal framework that fails to provide equal rights in various aspects of life. This gap creates a sense of uncertainty and anxiety for many same-sex couples, who are frequently enough left navigating an ambiguous legal landscape.Key issues they face include:
- Recognition of Rights: Without formal recognition,same-sex couples may struggle with inheritance issues,property rights,and parental rights.
- Healthcare Access: many couples may find themselves unable to make critical health decisions for their partners during medical emergencies.
- Social Stigmas: Persistent societal attitudes can lead to discrimination,affecting both personal relationships and professional opportunities.
Moreover, the path forward may be further intricate by the need for advocacy and awareness-raising among both the public and lawmakers. Engaging with local communities to promote understanding and acceptance of same-sex relationships will be crucial in overcoming these hurdles. As stakeholders push for legal reforms, the importance of grassroots activism cannot be overstated, as it can play a pivotal role in shifting perceptions and fostering a more inclusive society. Essential action points include:
- Legal Reform Initiatives: Advocates are urged to push for legislation that supports equal rights and protections for same-sex couples.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educational programs aimed at dismantling stereotypes can cultivate a more favorable cultural climate.
- Alliances with Other Movements: Collaborating with women’s rights and human rights organizations can amplify efforts for inclusive change.
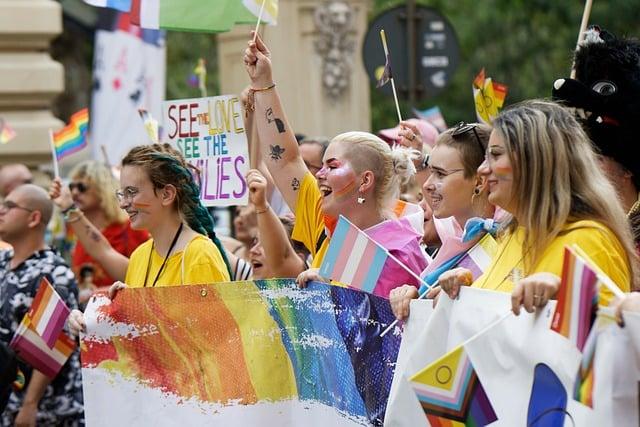

Recommendations for Advocacy: Strengthening Support Networks and Legal Frameworks
To effectively advocate for the progression of same-sex marriage and associated rights in Thailand and the broader Southeast Asian region, it is indeed critical to strengthen support networks and legal frameworks. Engaging local communities, civil society organizations, and international partners can amplify efforts towards equality. Key strategies include:
- Building Alliances: Foster partnerships among NGOs,LGBTQ+ groups,and legal entities to create a unified front,sharing resources and expertise.
- Enhancing Legal Literacy: Educate the public and stakeholders about existing laws and rights, emphasizing the importance of legal recognition for same-sex marriage.
- Advocacy Training: Provide workshops to empower community advocates with skills in lobbying, public speaking, and negotiation with government entities.
Additionally,developing a robust legal framework is paramount for ensuring lasting protection and recognition of same-sex unions. This can be achieved through:
- Legislative Proposals: Collaborate with lawmakers to draft inclusive policies that recognize same-sex marriage while addressing broader human rights issues.
- Court Cases: Support strategic litigation that challenges discriminatory laws and practices, setting legal precedents for equality.
- International Advocacy: Engage with global institutions to leverage international pressure on local governments for reform.
| Support strategy | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Building Alliances | Unified advocacy efforts |
| enhancing Legal Literacy | Informed communities |
| Legislative Proposals | inclusive marriage laws |
| Court Cases | Legal precedents for equality |

The Economic Implications of Marriage Equality: Boosting Tourism and International relations
As Thailand paves the way for marriage equality in Southeast Asia, the economic implications are becoming increasingly evident. By embracing same-sex marriage, the country is not just making a progressive social statement; it is also positioning itself as a premier travel destination for LGBTQ+ tourists. This demographic tends to have significant disposable income, and their presence can substantially uplift local economies. The potential benefits include:
- Increased hotel bookings: More couples traveling for weddings or honeymoons could fill up hotels and resorts.
- Enhanced local businesses: Restaurants, shops, and entertainment venues woudl likely see a boost in sales.
- Diverse event tourism:
– pride festivals
– LGBTQ+ conventions
– Wedding expos can enhance annual tourism rates.
Moreover,the progressive stance on marriage equality serves as a diplomatic tool,strengthening Thailand’s international relations. By aligning with globally recognized human rights principles, Thailand can improve its standing in the international community. As many countries either lag behind or resist the movement toward equality,Thailand’s leadership in this arena opens doors for new partnerships,trade agreements,and cultural exchanges. Key areas of impact include:
- attraction of international events: Thailand could host global LGBTQ+ events, fostering goodwill and collaborations.
- Strengthening regional ties: Leading by example can encourage neighboring nations to reconsider their policies.
- foreign investments: A progressive image can attract investments from companies valuing inclusivity and diversity.
to sum up
Thailand’s progressive stance on same-sex marriage marks a significant departure from the traditional norms prevalent in Southeast Asia,positioning the kingdom as a potential beacon of LGBTQ+ rights in the region. By pioneering legal frameworks that support marriage equality, Thailand not only challenges longstanding cultural taboos but also sets a precedent that may inspire neighboring countries to reconsider their own policies. This evolving landscape highlights the complex interplay between societal values,political will,and individual rights,suggesting that the fight for equality is far from over. As Thailand moves forward, the ultimate impact of these changes will be closely watched, serving as both a reflection of local sentiment and an indicator of broader regional trends. Whether Thailand will lead the way in fostering a more inclusive environment for all its citizens remains to be seen, but one thing is clear: the conversation around same-sex marriage in Southeast Asia is gaining momentum, and Thailand is at the forefront of this transformative movement.