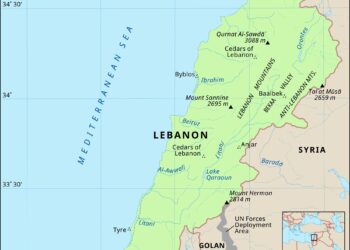
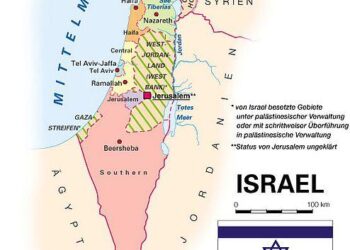
In a important advancement in the ongoing maritime tensions between Israel and Lebanon, new gas licenses have been approved for exploration in contested waters along their maritime border. This decision, announced by Israeli authorities, marks a pivotal moment in a complex geopolitical landscape characterized by energy disputes, national security concerns, and international diplomatic efforts. The Washington Institute reports that the approvals could lead to increased exploration and potentially lucrative discoveries in the Eastern Mediterranean, an area rich in natural gas reserves. As both nations grapple with economic challenges and energy needs, the implications of this move extend beyond mere resource extraction, potentially reshaping bilateral relations and impacting regional stability. In this article, we will delve into the details surrounding the new gas licenses, the historical context of the maritime border dispute, and the broader implications for Israel, Lebanon, and their neighboring nations.
Impact of New Gas Licenses on Regional Energy Dynamics
The recent approval of new gas licenses along the Israel-Lebanon maritime border marks a significant shift in the dynamics of regional energy production and consumption. This development not only alters the existing geopolitical landscape but also raises important questions about resource management and cooperation. The upcoming commercial activities are expected to lead to the following outcomes:
- Increased Energy Security: Countries in the region may bolster their energy independence, reducing reliance on external suppliers.
- Market Opportunities: The licensing opens doors for both local and foreign investments, paving the way for competitive energy markets.
- Potential for Cooperation: Natural gas could serve as a catalyst for improved relations between Israel and Lebanon, fostering dialog around shared interests.
Moreover, the new licenses may promote economic growth as nations explore the extraction and exportation of resources.Though, the potential risks associated with heightened tensions cannot be ignored. It is crucial that stakeholders consider the following challenges:
- Environmental Concerns: The environmental impact of drilling operations may provoke local opposition and regulations.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Conflicts over maritime boundaries could escalate if not managed diplomatically.
- Technical expertise: Regional players need to ensure access to technology and expertise for sustainable resource management.
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Energy Security | Increased self-sufficiency |
| Investment | Attraction of foreign capital |
| Cooperation | Possible rapprochement between nations |
| Environmental | Growing concerns and regulations |
| Tensions | Possibility of conflict escalation |

Legal Implications of the Israel-Lebanon Maritime Border Dispute
The maritime border dispute between Israel and Lebanon has intricate legal implications that are pivotal to understanding the broader geopolitical landscape of the region. The contested waters are primarily significant due to their potential hydrocarbon resources, which have drawn international attention and investments. As various entities invest in gas exploration and production amid the disputes, the legal framework surrounding territorial waters and exclusive economic zones (EEZ) becomes critical. These areas are governed by international law, particularly the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which outlines the rights of nations concerning maritime boundaries but does not provide a straightforward resolution for bilateral disputes.
In recent agreements and negotiations, both countries have engaged in diplomacy backed by international mediation, which has led to the delineation of maritime rights yet remains fraught with contentious issues. Key factors influencing the legal discourse include:
- Historical Claims: Both nations assert historical rights over the conflicting maritime areas, complicating negotiations.
- International Treaties: Existing treaties and prior agreements play a crucial role in legitimizing specific maritime claims.
- Foreign Interests: The involvement of international companies in gas exploration raises questions of sovereignty and the enforcement of any legal framework.
the resolution of these legal implications is not merely a matter of local or regional interest but entails ramifications for energy security, economic development, and international relations. While the pursuit of new gas licenses reflects a proactive approach to leveraging natural resources, the underlying legal complexities necessitate a careful navigation of diplomacy, ensuring that any exploration efforts do not exacerbate tensions but rather pave the way for cooperative solutions.

Economic Potential of Gas Developments for Both Nations
The recent decision to proceed with new gas licenses along the Israel-Lebanon maritime border signifies a strategic turning point for both nations, known for their complex political relationships but sharing precarious economic landscapes. As exploration and development activities commence, the potential benefits could be vast and multifaceted. Economic chance will arise from increased energy security, job creation, and potential revenue streams for both countries. Key factors include:
- Revenue Generation: Offshore gas reserves could lead to significant fiscal inflows.
- Energy Independence: Enhanced local energy production may reduce reliance on imports.
- Regional Cooperation: Joint ventures could foster improved diplomatic ties.
Additionally, the potential for gas exports presents a promising horizon. With international gas prices fluctuating and the global demand for energy rising, both nations could exploit these maritime resources to secure a foothold in the energy market. This opportunity is not merely about immediate financial gain; it also paves the way toward long-term investment in infrastructure and technology, which could further stimulate economic growth. Key considerations include:
| Aspect | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Job Creation | Thousands of jobs in exploration and production. |
| Foreign Investment | Attraction of international stakeholders. |
| infrastructure Development | Need for ports, pipelines, and energy facilities. |

Strategic Responses from Regional and International Stakeholders
The recent decision to proceed with new gas licenses along the Israel-Lebanon maritime border has triggered a wave of strategic responses from various regional and international stakeholders. Israel, seeking to reinforce its energy independence, has responded positively, emphasizing the importance of these licenses for enhancing its natural gas production and export potential. Simultaneously occurring, Lebanon finds itself in a precarious position, grappling with internal political turmoil and external pressures that complicate its ability to negotiate effectively over maritime rights. The Lebanese government has expressed concern regarding the implications of Israel’s actions on its territorial claims, calling for international support to mediate the escalating tensions.
International stakeholders are also keenly observing the developments, recognizing the broader geopolitical implications of increased gas exploration in the region. The United States has taken a proactive stance, advocating for dialogue between Israel and Lebanon while concurrently facilitating discussions with key players such as Russia and the European Union, who have vested interests in the stability of energy supplies from the Eastern Mediterranean. Notably, regional actors like Egypt and Qatar are positioning themselves to play a mediating role, leveraging their own energy capabilities to foster cooperation and mitigate conflict risks. The diverse responses underscore the complexity of the situation,as various interests collide in a region long known for its geopolitical volatility.
| Stakeholder | Response |
|---|---|
| Israel | Positive outlook on energy independence and export potential. |
| Lebanon | Calls for international support to assert territorial claims. |
| United States | Encourages dialogue and supports negotiation efforts. |
| Egypt / qatar | Willing to mediate and leverage energy capabilities. |
| European Union | Interest in stability and energy supply continuity. |

Recommendations for Diplomatic Engagement and Conflict Resolution
In light of the recent development concerning gas licenses along the Israel-Lebanon maritime border, it is indeed vital for both nations to prioritize diplomatic channels to mitigate tensions and potentially foster cooperation. Engaging in a robust dialogue can pave the way for a better understanding of mutual interests and shared concerns.Stakeholders should consider the following strategies:
- Facilitating Multilateral Talks: Involving regional players and international organizations can definitely help ensure that concerns are addressed comprehensively and constructively.
- Establishing Confidence-Building Measures: Initiatives that promote interaction,such as joint maritime patrols,can reduce misunderstandings and foster trust.
- Encouraging Economic Cooperation: Collaborating on energy projects, including shared exploration initiatives in contested waters, may transform competition into collaboration.
Additionally, the role of external mediators should not be underestimated. The following could enhance the chances of successful conflict resolution:
| Mediator | Proposed Role |
|---|---|
| United Nations | Facilitate discussions and monitor agreements |
| European Union | Provide economic incentives for cooperation |
| United States | Offer diplomatic support and strategic insights |

Future Outlook for Energy Cooperation in the Eastern Mediterranean
The recent developments in the maritime border negotiations between Israel and Lebanon signal a potential shift in the energy landscape of the Eastern Mediterranean. With new gas licenses being issued, both nations are poised to capitalize on vast undersea resources.observers note that this could pave the way for improved bilateral relations,as economic interests often drive political cooperation. Key factors influencing the future of energy collaboration include:
- Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing clear legal parameters to govern cooperation can reduce tensions and create a stable investment surroundings.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: The interplay of regional powers may affect negotiations, with external influences shaping the outcome of energy partnerships.
- Technological Innovations: Advances in exploration and extraction technology can make previously unviable resources accessible, enhancing cooperation opportunities.
Looking ahead, the interplay between energy resource development and regional diplomacy will be crucial. Collaboration on energy infrastructure could serve as a foundation for broader agreements spanning security and trade. Potential areas for collaborative efforts include:
| Area of Cooperation | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Joint Exploration | Shared risks and costs, optimized resource extraction. |
| Infrastructure Development | Enhanced connectivity, economic growth, stability. |
| environmental Stewardship | Collaborative efforts to minimize ecological impacts. |
Closing Remarks
the issuance of new gas licenses in the contested maritime border between Israel and Lebanon marks a significant step in the evolving landscape of energy politics in the Eastern Mediterranean. As both nations seek to capitalize on their natural resources, the implications extend beyond economic benefits, potentially influencing regional stability and international relations.The intricacies surrounding these licenses reflect broader geopolitical tensions and underscore the urgency for diplomatic dialogue. As developments unfold,stakeholders from both sides will need to navigate this complex terrain carefully,balancing national interests with the need for cooperation in a resource-rich but contentious area. The coming months will be critical in determining how these new licenses will reshape not only the energy landscape but also the diplomatic interplay in the region.