As the United States navigates the complexities of its foreign policy landscape, the prospect of a second Trump management invites a critical reevaluation of strategies toward global hotspots, particularly Myanmar. The ongoing political turmoil and humanitarian crises in the Southeast Asian nation necessitate a fresh approach that balances national interests with ethical considerations. This article delves into the Stimson center’s analysis, highlighting the pressing need for a recalibrated U.S. policy that addresses escalating challenges while promoting democratic values and regional stability. By exploring historical contexts, current developments, and potential diplomatic pathways, we aim to illuminate the intricate dynamics at play and offer insights into how the U.S. can effectively engage with Myanmar in a rapidly changing geopolitical surroundings.
Rethinking Strategic Engagement with Myanmar Under a Trump Administration

The complex political landscape in myanmar presents a unique challenge for US foreign policy, particularly under a second Trump administration. Any new approach will have to navigate competing interests, including human rights concerns and strategic economic partnerships. Moving forward, policymakers must prioritize a multi-faceted engagement strategy that balances diplomatic pressure with targeted support for civil society initiatives. Key focus areas should include:
- Human Rights Advocacy: Reinforcing commitments to human rights by supporting organizations that monitor abuses.
- Economic Leverage: Utilizing trade policies to incentivize democratic reforms.
- Regional Cooperation: Collaborating with ASEAN nations to address regional stability issues.
- Engagement with Ethnic Minorities: Ensuring that minority voices are included in the dialog to foster a more inclusive political environment.
Moreover, understanding Myanmar’s geopolitical dynamics is essential for shaping an effective policy. With growing influence from China and the risk of increasing authoritarianism, the US must assert its presence strategically. Establishing a bilateral dialogue that is consistent and open will be crucial. The US should consider:
| Strategy | Objective |
|---|---|
| Diplomatic Engagement | To create a platform for addressing pressing issues and enhancing mutual understanding. |
| Economic Assistance | To provide targeted support for sustainable growth and improve livelihoods. |
| Security Partnership | To enhance capacity building for democratic governance and rule of law. |
By reassessing the engagement strategy, the US can perhaps redefine its role in Myanmar, creating an possibility for meaningful change while mitigating risks associated with an increasingly complex regional environment.
Evaluating Human Rights Concerns in US-Myanmar Relations

The evolving dynamics of US-Myanmar relations necessitate a thorough examination of human rights conditions within Myanmar, especially in light of the ongoing political crisis and military governance. In recent years, Myanmar has been marked by severe human rights violations, including ethnic cleansing, suppression of free speech, and violent crackdowns on protests. In this very way, the US must navigate its foreign policy with heightened awareness of these grave concerns. A critical aspect of this evaluation includes acknowledging the plight of vulnerable populations,such as the rohingya,who have faced systematic discrimination and violence. Ensuring that US policies do not inadvertently support oppressive regimes is essential for fostering a more just international community.
Furthermore, any reevaluation of US engagement must consider the implications of sanctions and diplomatic measures designed to hold the military junta accountable. Key areas of focus include:
- Ensuring openness in US diplomatic efforts
- Coordinating with regional allies to enhance collective pressure
- Supporting civil society organizations within Myanmar
- Promoting humanitarian assistance for affected populations
Ultimately, advancing human rights should not merely be an ancillary objective but rather a central tenet of US policy towards Myanmar. This approach will help to reinforce international norms and potentially pave the way for a more stable and democratic future in the region.
Economic Sanctions and Their Impact on Myanmar’s Civil Society

The imposition of economic sanctions on Myanmar has brought about profound challenges for civil society within the country. These restrictions, aimed at pressuring the military junta, have inadvertently stifled the very civilian voices they seek to empower. Critical sectors such as healthcare, education, and human rights advocacy face diminishing resources, severely hampering the capacity of non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and grassroots movements to operate effectively. Moreover, the sanctions may have unintentionally bolstered a humanitarian crisis by limiting aid and support from international actors, thereby extending the suffering of ordinary citizens while the military continues to consolidate its power.
Moreover, the repercussions of the sanctions extend beyond mere economic implications; they have led to a chilling effect on activism and civic engagement. With rampant repression and the threat of persecution looming over dissenters, many civil society members are compelled to operate in the shadows, which undermines their effectiveness. The following points highlight some critical considerations regarding the effects of these sanctions on civil society:
- Resource depletion: Restrictions hinder funding and essential supplies for NGOs.
- increased Repression: The military government employs the sanctions as justification for heightened crackdowns on dissent.
- Isolation of Voices: Key activists and organizations struggle to maintain international relations and support.
- Impact on Vulnerable Populations: Sanctions have direct consequences on civil welfare and access to basic services.
Promoting Democratic Resilience: Supporting Local Governance

Enhancing democratic resilience in myanmar necessitates a strong emphasis on local governance, enabling communities to take charge of their political landscape. The United States can play a transformative role by providing training and resources that empower local leaders and institutions. Supporting initiatives that encourage community participation, transparency, and accountability fosters an environment where citizens feel invested in their governance. This grassroots approach cultivates a sense of ownership among the populace and can serve as a bulwark against authoritarianism.
Key strategies for promoting robust local governance include:
- Capacity Building: Equipping local authorities with the necessary skills and knowledge to manage resources effectively.
- Decentralization Efforts: Encouraging a shift of power from central to local institutions, which can increase responsiveness and citizen engagement.
- community Engagement Programs: Implementing initiatives that encourage dialogue between local leaders and their constituents to ensure policies reflect community needs.
| Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Capacity Building | Enhances local governance efficiency and effectiveness |
| Decentralization Efforts | Increases citizen trust and participation in governance |
| Community engagement Programs | Promotes transparency and accountability in local decision-making |
Regional Dynamics: The Role of ASEAN in US Policy Formulation

In the complex landscape of Southeast Asian geopolitics, ASEAN emerges as a critical player in shaping US foreign policy, particularly towards Myanmar. The association serves as a platform for fostering dialogue, collaboration, and consensus among its member states.As the Biden administration has shown a keen interest in multilateralism, a second Trump administration may likely shift its dynamics by leveraging ASEAN diplomacy to galvanize regional support around US interests. Such an approach could involve:
- Enhanced Diplomatic Engagement: Increasing high-level dialogues between US officials and ASEAN leaders to address regional security concerns and human rights issues in myanmar.
- Economic Cooperation: Promoting trade relations that benefit both the US and ASEAN nations, ensuring that economic aid aligns with support for democratic movements in Myanmar.
- strategic Partnerships: Strengthening security partnerships within ASEAN to counter chinese influence while encouraging collective action on Myanmar’s political crisis.
For the US to effectively navigate its policy towards Myanmar, it must also recognize ASEAN’s unique position and its varying member state perspectives on the coup and subsequent humanitarian issues. there is potential for collaboration on efforts to facilitate humanitarian aid and democratic transitions in Myanmar. This could be operationalized through a coordinated response table, highlighting each ASEAN member’s role:
| ASEAN member | Potential Role |
|---|---|
| Indonesia | lead regional dialogues |
| Thailand | Provide humanitarian assistance |
| singapore | Facilitate investments |
Future Prospects: Building a Sustainable Framework for US-Myanmar Ties
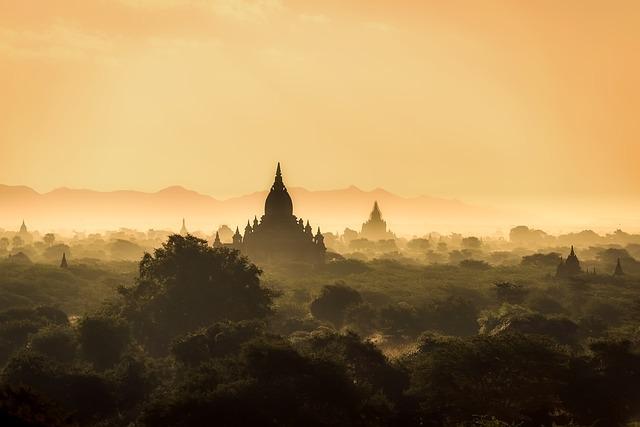

The future of US-Myanmar relations hinges on developing a thorough and sustainable framework that prioritizes mutual respect and long-term benefits for both nations. This framework must embrace a multidimensional approach, fostering collaboration across various sectors, including economic development, human rights, and regional security. Key strategies to achieve this could involve:
- Enhancing trade relations by negotiating favorable agreements that benefit both economies.
- Promoting cultural exchanges to strengthen people-to-people ties and mutual understanding.
- Supporting democratic institutions to ensure a stable political environment conducive to growth.
In addition, the prioritization of sustainability is critical in forging a robust partnership. this involves not only environmental considerations but also the sustainability of political practices and governance structures. in this very way, the implementation of joint initiatives focused on climate resilience, renewable energy, and community development should be on the agenda.A proposed action plan might include:
| Initiative | Goal | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| climate Action Partnerships | Reduce CO2 emissions | 2024-2026 |
| Economic Workshops | Skill training for sustainable jobs | 2023-2025 |
| Human Rights Advocacy | Strengthen rule of law and justice | Ongoing |
Final Thoughts
the prospect of a second Trump administration presents a critical juncture for U.S. foreign policy towards Myanmar. As the political landscape evolves, it is imperative for policymakers to reassess existing strategies and take into account the complex realities on the ground. Engaging with Myanmar’s crisis—marked by civil unrest and humanitarian challenges—requires a nuanced approach that balances diplomatic pressure with support for democratic movements.
The Stimson Center’s insights underscore the importance of collaborative efforts with regional allies and civil society groups to foster meaningful dialogue and sustainable solutions. A reimagined U.S.policy could not only promote stability in Myanmar but also enhance American credibility on the global stage. As the international community watches closely, the choices made in Washington will undoubtedly resonate beyond the borders of Myanmar, shaping the future of U.S. engagement in Southeast Asia.
As this new chapter unfolds, ongoing dialogue and informed strategies will be essential in addressing one of the most pressing humanitarian crises of our time.















![ISWK[Cambridge] Students Bring Glory to Oman at the 2nd Asian Yogasana Sport Championship! – Times of Oman](https://asia-news.biz/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/165927-iswkcambridge-students-bring-glory-to-oman-at-the-2nd-asian-yogasana-sport-championship-times-of-oman-120x86.jpg)