As the climate crisis intensifies, its ripple effects are being felt across various sectors worldwide, with Pakistan’s bee population and honey trade emerging as particularly vulnerable.Onc celebrated for producing some of the finest honey varieties in the region, Pakistan is now grappling with the challenges posed by rising temperatures, erratic weather patterns, and habitat loss—all of which threaten the delicate ecosystems that support bee populations.This alarming trend not only jeopardizes the livelihoods of local beekeepers but also raises concerns about food security and biodiversity in a country heavily reliant on agriculture. This article delves into the intricate relationship between climate change and Pakistan’s apiculture industry, exploring the implications for both the environment and the economy, while highlighting the urgent need for sustainable practices in the face of an escalating global crisis.
Impact of climate Change on Pollinator populations in Pakistan
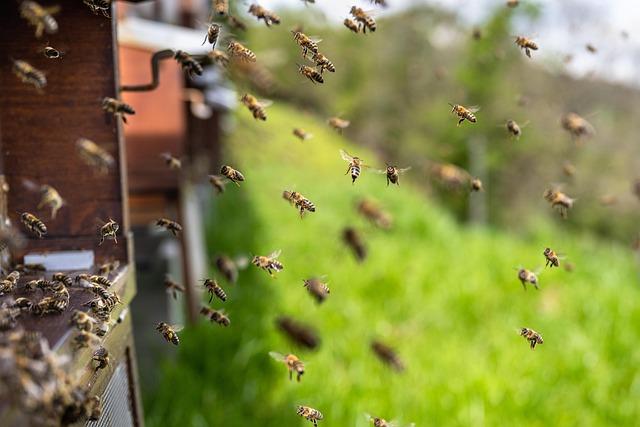
The ongoing climate crisis poses a notable threat too the delicate balance of pollinator populations in Pakistan,particularly affecting vital species like bees.these essential insects are fundamental not only for biodiversity but also for the agricultural economy.Changes in temperature and increased frequency of extreme weather events have led to habitat loss, altering the natural behaviors and life cycles of these pollinators.This disruption has resulted in a decline in their populations, which is deeply concerning for farmers who rely on bee pollination for crops such as fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
Moreover, the implications for local honey production are dire. As the climate reshapes floral diversity, bees struggle to find the necessary food sources, negatively impacting honey yield and quality. the economic repercussions are equally significant, threatening the livelihoods of beekeepers and the sustainability of the honey trade in the region. Key statistics reveal the growing concerns:
| Year | Estimated Bee Population (millions) | Honey Production (tons) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 80 | 35,000 |
| 2021 | 70 | 30,000 |
| 2022 | 65 | 25,000 |
As these figures indicate, there is a troubling downward trend in both bee populations and honey production. Addressing the effects of climate change is critical to safeguarding not just the pollinators but also the communities that depend on them.Sustainable agricultural practices, habitat restoration, and raising awareness about the importance of pollinators are essential steps to mitigate these challenges and ensure a resilient ecosystem in Pakistan.

Consequences for Agriculture and Food Security
The decline in bee populations due to climate change poses significant risks to agricultural productivity and food security in Pakistan. As bees are vital pollinators, their dwindling numbers could lead to a reduction in crop yields, particularly for fruits and vegetables that rely heavily on insect pollination. This could result in a domino effect on food supply chains, driving up prices and making these essential foods less accessible to the population. Farmers may find themselves facing tougher challenges as they attempt to adapt to these ecological changes, possibly leading to an increased reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which can further exacerbate environmental degradation.
The impact of a declining honey trade is also profound, affecting livelihoods and economies connected to this vital industry. Honey production not only generates income for local beekeepers but supports rural economies by providing jobs related to production, packaging, and distribution. The threats posed by climate change could result in diminishing honey yields, thus pushing prices higher and making local honey less competitive against imported options. This situation could jeopardize the economic stability of rural communities that depend on beekeeping as a primary source of income, leading to increased poverty and food insecurity among vulnerable populations.

The Economic Significance of the honey Trade in Pakistan
The honey trade in Pakistan holds considerable economic significance, contributing to both rural livelihoods and the national economy. As honey production heavily relies on the country’s diverse flora and climate, regions such as Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Punjab have become hotspots for apiculture. The sector supports thousands of beekeepers who engage in both small-scale and commercial production. Not only does honey offer a lucrative source of income, but it also enhances agricultural productivity through pollination, thus benefiting crop yields. It is estimated that the honey industry generates an annual revenue of over $50 million,playing a pivotal role in rural development and poverty alleviation.
Furthermore, the potential for Pakistan to expand its honey trade in international markets is significant. The country is endowed with unique floral varieties that produce high-quality, organic honey, appealing to health-conscious consumers globally. However,to maximize this potential,the industry must navigate challenges such as inconsistent quality,lack of proper branding,and increased competition from other honey-producing nations. Addressing these challenges could lead to an increase in exports, which currently linger around 3,000 tons annually. By investing in sustainable practices and improving supply chain efficiencies, Pakistan has the possibility to elevate its status in the global honey market.

strategies for Bee Conservation Amidst Climate Threats
The challenge posed by climate change on bee populations requires immediate and multifaceted approaches to safeguard these vital pollinators. Habitat restoration plays a critical role in bee conservation. By creating diverse ecosystems,including wildflower meadows and native plant gardens,we can provide essential food and shelter for bees. Additionally, reducing pesticide use is paramount; opting for organic farming practices not only supports bee health but also promotes biodiversity. Communities can engage in beekeeping education programs to empower local citizens with the knowledge of sustainable practices and the importance of bees in agricultural systems.
Collaboration among stakeholders is vital to address this pressing issue effectively.Government agencies should implement policies that prioritize bee conservation, including fostering partnerships with farmers and conservation organizations. Public awareness campaigns can definitely help educate citizens about the importance of bees and encourage individual actions like creating bee-amiable spaces in urban areas. Community gardens, green rooftops, and pollinator highways can serve as crucial habitats. Together, these strategies not only combat climate threats but also strengthen local economies dependent on the honey trade, ensuring a sustainable future for both bees and beekeepers.

Policy Recommendations for Sustainable Beekeeping Practices
To safeguard Pakistan’s honey industry and promote environmental stewardship,it is indeed imperative to implement comprehensive policies that address the challenges posed by climate change. Key strategies could include:
- Funding for Research: Allocate resources to study the impact of climate variations on local bee populations and honey production.
- Training and Education: Develop programs for beekeepers focused on sustainable practices, climate adaptation, and biodiversity preservation.
- Incentives for Organic Practices: Offer financial benefits to beekeepers who adopt organic and environmentally friendly methods, promoting healthy ecosystems.
Additionally, local governments should facilitate collaboration between stakeholders, including farmers and conservationists, to ensure a holistic approach to agriculture and apiculture. Efforts could include:
- Community Engagement: Foster community-based initiatives to increase awareness about the essential role of bees in ecosystem health.
- bee Habitat Protection: Establish protected areas that support wild pollinators and mitigate habitat loss due to urbanization and agricultural expansion.
- Policy Integration: Ensure that national agricultural policies consider the interplay between beekeeping and the broader impacts of climate change.

Community Engagement and Education in Protecting Pollinators
Engaging local communities is vital in the fight to protect pollinators, particularly in a country like Pakistan where climate change poses a serious threat to ecosystems and agricultural livelihoods. Educational initiatives can help raise awareness about the crucial roles that bees and other pollinators play in food production and biodiversity. Efforts to mobilize communities can include:
- Workshops on sustainable agricultural practices that promote the health of pollinator populations.
- School programs that teach children about the importance of bees and the environment.
- Community gardens where citizens can practise pollinator-friendly gardening techniques.
Moreover, fostering partnerships between local beekeepers, environmental organizations, and government bodies can enhance knowledge sharing and resource allocation. Collaborative projects might focus on the following areas:
| Area of Focus | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Pollinator Habitat Restoration | Enhances local biodiversity and supports bee populations. |
| Research and Monitoring | Provides data to assess the health of pollinator communities over time. |
| Organic Farming Initiatives | Reduces chemical usage, benefiting both pollinators and soil health. |
The Way Forward
As climate change continues to alter the delicate balance of ecosystems globally, its profound implications for Pakistan’s bees and the honey trade become increasingly apparent. The threats to these vital pollinators, driven by fluctuating temperatures, erratic weather patterns, and shrinking habitats, underscore a broader environmental crisis that not only jeopardizes biodiversity but also threatens livelihoods and food security in the region. As beekeepers and environmentalists strive to adapt and find innovative solutions to preserve bee populations, the need for sustainable practices and policies has never been more urgent. Addressing these challenges will require a concerted effort from government bodies,local communities,and international organizations to prioritize the protection of pollinators. The future of Pakistan’s honey industry—and the health of its ecosystems—largely depends on our collective commitment to combating the climate crisis. As we reflect on these pressing issues, it is clear that the fate of the bees is intertwined with our own, reminding us that safeguarding our environment is essential for a prosperous future.