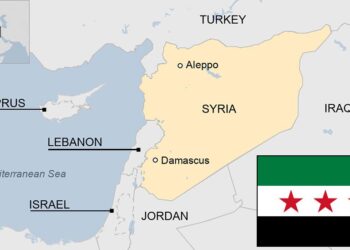
In recent months, the United States has grappled with the implications of a foreign aid freeze impacting its strategic interests in Syria. As the situation in the region remains fraught with complexity—from ongoing conflict and humanitarian crises to the influence of rival powers—the decision to halt financial assistance raises notable concerns. This article delves into the potential repercussions of this aid freeze, highlighting how it could undermine U.S. efforts to stabilize the region, support local communities, and counteract the influence of adversarial actors.With insights from experts at the Atlantic Council, we explore the delicate balance of power in Syria and the critical role that U.S. support plays in shaping both regional dynamics and American foreign policy objectives.
Impact of Foreign Aid Freeze on Humanitarian Efforts in Syria
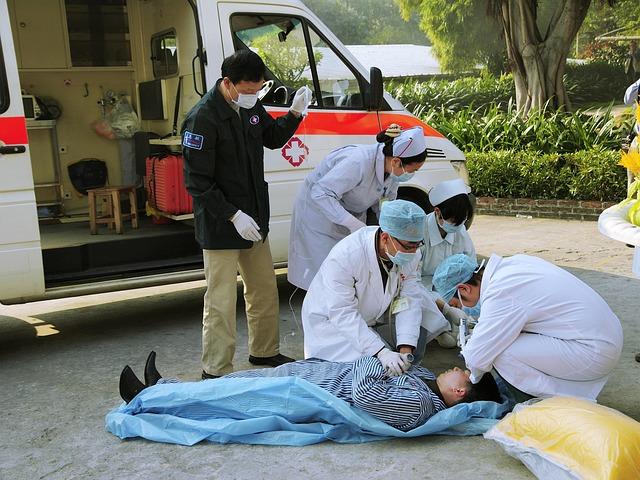
The suspension of foreign aid to Syria has profound implications for the humanitarian landscape, exacerbating an already dire situation for millions of vulnerable civilians. With aid agencies facing operational constraints, the fallout is evident in several key areas:
- Food Insecurity: The disruption of food supplies has led to a significant rise in malnutrition rates, especially among children and the elderly.
- Healthcare Access: Clinics and hospitals that rely on foreign funding are struggling to provide basic medical services, increasing the risk of disease outbreaks.
- Infrastructure Deterioration: the inability to maintain essential services like clean water and sanitation has heightened the risk of public health crises.
Moreover, the aid freeze not only affects immediate humanitarian efforts but also undermines long-term stability objectives in the region. The trends indicate that:
| Indicator | Pre-Aid Freeze | Post-Aid Freeze |
|---|---|---|
| Refugee Return Rates | Trending Upward | Declining |
| Healthcare Facility Operations | 80% Functional | 40% Functional |
| Child Malnutrition Rates | 5% severe | 15% severe |
This growing humanitarian crisis could incite further instability in the region, hindering US interests by fostering environments conducive to extremism and unrest. As aid organizations brace for the long-term consequences of this freeze,the need for a reevaluation of aid policies becomes increasingly urgent.
Strategic Consequences for Regional Stability and Security

The implications of the foreign aid freeze extend well beyond immediate humanitarian concerns, presenting multiple risks to the overall stability and security of the region.A significant reduction in U.S. funding could lead to increased instability in Syria, perhaps allowing extremist groups to gain a foothold. This situation could result in a resurgence of organized violence, exacerbating an already complex conflict landscape. Furthermore, the vacuum created by diminished U.S. involvement may encourage rival powers, such as Russia and iran, to further assert their influence, raising the stakes in the geopolitical chess game of the Middle East.
Moreover, the freeze could negatively impact local governance structures, crucial for maintaining law and order in a fragmented society. Weakening these institutions may lead to a breakdown of social contracts between citizens and their governing bodies. Key factors to consider include:
- Increased Humanitarian Needs: Without aid, the suffering of civilians is highly likely to escalate, leading to further displacement and radicalization.
- Potential for inter-Group Conflicts: Resource scarcity might heighten tensions among ethnic and religious groups, increasing the propensity for violence.
- Loss of U.S. Soft Power: A retreat from aid could diminish U.S.credibility as a reliable partner in peacebuilding efforts.
Economic Ramifications for Syrian Reconstruction and Development

The recent freeze on foreign aid aimed at Syria has profound implications for the country’s reconstruction and development, affecting not only the local economy but also broader geopolitical interests. The interruption of financial support is likely to exacerbate existing economic challenges, leading to potential instability in the region. The consequences of this aid freeze can be categorized as follows:
- Increased Humanitarian Needs: With dwindling resources, the humanitarian crisis is expected to worsen, resulting in greater needs for food, healthcare, and shelter.
- Unemployment Surge: The halt in funding for development projects will likely trigger a steep rise in unemployment, pushing more individuals into the already strained informal economy.
- Public Services Strain: Public services such as education and healthcare may falter, leading to decreased living standards and increased social discontent.
Considering these economic challenges, the necessity for a strategic approach to rebuilding the Syrian economy is critical. The implications of neglecting this reconstruction are twofold, not only jeopardizing the lives of millions but also threatening U.S. interests in the region. The potential fallout includes:
| Risk Factor | Potential impact |
|---|---|
| Increased Extremism | Economic hardship can fuel extremist ideologies as disenfranchised individuals seek choice means to express their grievances. |
| Regional Instability | Unaddressed economic woes may lead to spillover effects in neighboring countries, worsening the regional security situation. |
Recommendations for Reassessing US Foreign Aid Policies
As the tensions in Syria continue to evolve, it is crucial for the United States to reassess its foreign aid strategies to ensure that aid effectively supports stability and security in the region.A significant part of this reassessment should involve a transparent evaluation of current aid allocations and their impacts. Key considerations could include:
- Targeting Humanitarian Needs: Assessing how aid can be better directed to address the urgent needs of displaced populations and vulnerable communities.
- Enhancing Accountability: Establishing mechanisms to ensure that aid reaches its intended beneficiaries and does not support hostile or extremist groups.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with local organizations that have a deeper understanding of community needs and dynamics.
Moreover, a flexible approach to funding is essential, allowing the U.S. to respond swiftly to changes on the ground. This may involve shifting funding priorities based on real-time assessments of the political landscape. A potential framework for reassessing aid could include:
| Focus Area | Proposed Action | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| humanitarian Assistance | increase funding for NGOs | Improved access to food, water, and shelter |
| security Support | Provide training for moderate groups | Strengthened local governance and stability |
| economic Development | Invest in local businesses | Job creation and reduced unemployment |
By adopting a extensive and adaptive strategy, the united States can mitigate the risks associated with the current freeze on foreign aid and ensure that its policies are aligned with both humanitarian imperatives and national interests.
Long-term Implications for US Influence in the Middle East

The freeze on foreign aid to Syria could have profound ramifications not only for the country’s immediate stability but also for the broader dynamics of U.S. influence in the Middle East. As regional powers jockey for position in the wake of shifting alliances and internal unrest, the absence of American financial support may leave a vacuum that other nations are eager to fill. Iran and Russia have already established significant footholds in Syria, leveraging their connections to bolster their respective regional agendas. Without a sustained U.S. presence and commitment, the influence of these actors may deepen, potentially undermining decades of American diplomatic efforts in the area.
The ramifications extend beyond Syria’s borders, impacting U.S. credibility among allies and partners in the region. If the U.S. is perceived as retracting its support,countries like Jordan,Turkey,and Israel may find themselves questioning Washington’s reliability in their security arrangements. This erosion of trust can lead to:
- Fostering stronger ties between regional adversaries,
- Increased military cooperation among nations wary of U.S. intentions,
- And a shift in strategic partnerships that may favor autocratic regimes.
Ultimately, the freeze could catalyze a reevaluation of how the U.S. engages with the Middle East, prompting ally nations to pursue more autonomous foreign policies that do not align with American interests.
Collaborative Approaches to Mitigate Risks and Enhance Aid Effectiveness

As global crises continue to unfold, the need for collaborative approaches in aid delivery has never been more crucial. The freeze on foreign aid not only disrupts humanitarian efforts in Syria but also creates a vacuum where extremist ideologies can flourish. Collaborating with international partners and local entities can significantly enhance the effectiveness of aid by ensuring that resources are directed efficiently and reach those who need them most. In coordination with NGOs and intergovernmental organizations, the U.S. can foster a more comprehensive strategy that addresses immediate needs while building long-term stability.This involves:
- Coordination with Local actors: Engaging communities in the planning and execution of aid programs ensures that interventions are culturally sensitive and contextually relevant.
- Resource Sharing: Pooling resources with other nations can magnify impact, reducing redundancy in efforts and ensuring a wider reach.
- Continuous Evaluation: Implementing feedback mechanisms to adapt to changing conditions on the ground can enhance the transparency and accountability of aid delivery.
To further illustrate the potential benefits of these collaborative strategies, consider a comparison of potential outcomes based on varying levels of cooperation:
| Cooperation Level | Stability Index | Humanitarian effectiveness | Risk of Misallocation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Collaboration | 45 | 60% | High |
| Moderate Collaboration | 70 | 75% | medium |
| High Collaboration | 85 | 90% | Low |
This data highlights not only the value of joint efforts in improving stability and humanitarian outcomes but also the critical nature of reducing misallocation risks. It is indeed imperative for U.S. policymakers to recognize that a multifaceted approach to aid—integrating local knowledge,international partnerships,and adaptive strategies—can lead to a more sustainable impact in regions like Syria.
In Summary
the freeze on foreign aid to Syria not only endangers the delicate humanitarian landscape within the country but also poses significant risks to U.S. strategic interests in the region. As the humanitarian crisis deepens and extremist groups seek to exploit the ensuing instability,the repercussions of diminished U.S. support could have far-reaching effects on national security and diplomatic relations. The Atlantic Council’s analysis underscores the urgent need for a reassessment of current policies. To safeguard both Syrian civilians and U.S. interests, it is crucial for policymakers to navigate the complex terrain of foreign aid with a focus on sustainable solutions and collaborative international efforts. As the situation evolves, maintaining a proactive and nuanced approach to aid in Syria will be vital in addressing both humanitarian needs and geopolitical challenges.















![ISWK[Cambridge] Students Bring Glory to Oman at the 2nd Asian Yogasana Sport Championship! – Times of Oman](https://asia-news.biz/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/165927-iswkcambridge-students-bring-glory-to-oman-at-the-2nd-asian-yogasana-sport-championship-times-of-oman-120x86.jpg)