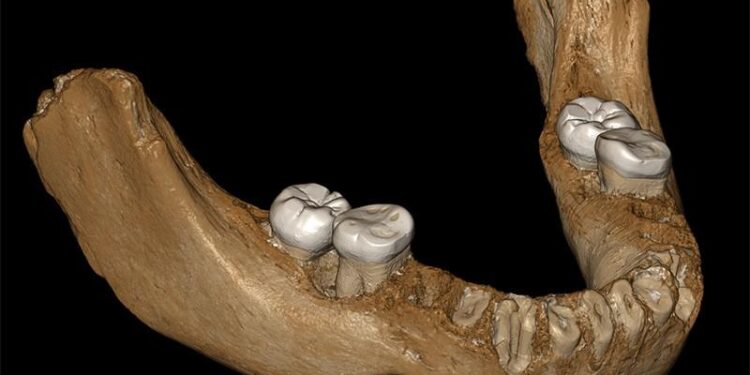
In a groundbreaking finding, scientists have identified the first Denisovan fossil found in Taiwan, illuminating the enigmatic history of our ancient relatives. This remarkable find not only deepens our understanding of the Denisovan lineage, known for its role in the early human family tree, but also challenges previous assumptions about their geographical range and interactions wiht other hominin species. The discovery, detailed in a recent study published by ScienceAlert, showcases the importance of Taiwan as a key location in the exploration of human evolution and the migratory patterns of early hominins. researchers are now poised to uncover the secrets hidden within this fossil,as they piece together the complex puzzle of our shared ancestry.
New Denisovan Fossil Unearthed in Taiwan Sheds light on Human Evolution
The recent discovery of a Denisovan fossil in Taiwan represents a groundbreaking addition to our understanding of human evolution. This find, characterized by distinct morphological features, provides critical insights into the existence and migratory patterns of these enigmatic relatives of modern humans. Researchers believe that this fossil may reveal important facts about how Denisovans adapted to their environments, as well as their interactions with other hominin species, including Neanderthals and early Homo sapiens. The analysis of the fossil suggests key adaptations that might have contributed to their survival in diverse habitats.
Key aspects of the fossil have led scientists to ponder its implications, including:
- Geographical Range: Previously thought to be limited to Siberia, this discovery pushes the known range of Denisovans further south.
- Genetic Interactions: The fossil opens avenues for exploring potential gene flow between Denisovans and other hominins.
- Adaptation Strategies: Detailed studies might shed light on how Denisovans thrived in different climates and landscapes.
As investigations progress,the fossil from Taiwan could reshape our understanding of the Denisovan lineage and its place within the broader narrative of human evolution. The ongoing research may reveal not only the biological aspects of these ancient humans but might also offer a glimpse into their social structures and survival strategies.
Insights into Denisovan Lifestyle and Habits from the Latest Discovery
The recent discovery of the first Denisovan fossil in Taiwan has offered archaeologists and anthropologists invaluable insights into the lifestyle and habits of these enigmatic ancient relatives of modern humans. Analysis of the fossil suggests that Denisovans exhibited a complex social structure similar to that of Neanderthals and early Homo sapiens. Emerging evidence indicates that they likely engaged in organized hunting expeditions, utilized a variety of tools, and developed a deep understanding of their surroundings, which included the careful selection of resources such as edible plants and animal prey.
Additionally, the findings have shed light on their cultural practices, including possible ritualistic behaviors and the use of pigments, indicating a desire for aesthetic expression or symbolic interaction. Genetic studies point toward interactions with local Homo sapiens populations,suggesting a degree of social integration and exchange. The Denisovans appeared to adapt remarkably well to varied climates and terrains, as indicated by remains discovered in caves across Southeast Asia. These adaptations reflect not only their resilience but also their innovative strategies in survival.
Implications for Future Research on Ancient Human Relatives and Migration Patterns
The discovery of the first Denisovan fossil in taiwan opens up exciting avenues for exploring the evolutionary journey of ancient human relatives, particularly their migration patterns across Asia.this finding prompts researchers to reassess existing models of human dispersal and to consider the potential interbreeding between Denisovans and other hominin species. As scientists delve into genetic analyses, it becomes crucial to investigate how these ancient populations might have adapted to different environments, which could provide insights into the resilience and adaptability of early human societies.
Future studies should focus on several key areas, including:
- Genetic Diversity: Examining how genetic variations among Denisovans and other ancient humans correlate with environmental changes.
- Archaeological Correlations: Integrating fossil evidence with artifacts to better understand migration routes and settlement patterns.
- Interdisciplinary Approaches: Utilizing genetic, archaeological, and climatic data to create comprehensive models of human evolution.
To facilitate these investigations, researchers may consider comparative studies across regions. The table below outlines potential sites for upcoming fieldwork that could complement findings from Taiwan:
| Location | Significance | Research Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Siberia | Known Denisovan sites | Genetic comparisons |
| Indonesia | Homo floresiensis discovery | Migration routes to Southeast Asia |
| south Asia | Fossil evidence of early humans | Cultural interactions and trade |
As the research field evolves, these implications will not only enhance our understanding of Denisovans and their contemporaries but also shed light on the complex tapestry of human migration and adaptation throughout history.
To Wrap It Up
As researchers continue to unravel the mysteries of our ancient relatives,the discovery of the first Denisovan fossil in Taiwan marks a significant milestone in the field of paleoanthropology. This remarkable find not only sheds light on the migratory patterns and habitats of these enigmatic hominins but also deepens our understanding of human evolution in the Asia-Pacific region. The implications of this discovery extend beyond Taiwan,inviting fresh examination of the Denisovans’ interactions with modern humans and Neanderthals across diverse landscapes.As scientists delve deeper into this fossil’s secrets, the ongoing examination promises to reshape our comprehension of the complex tapestry of human ancestry. With each new piece of evidence, we draw closer to answering the enduring questions about who our ancient relatives were and how they fit into the broader story of humanity. Continued research will there’s no doubt whatsoever uncover even more astounding revelations,highlighting the importance of fossil finds in illuminating the past and informing our understanding of human evolution today.