Introduction
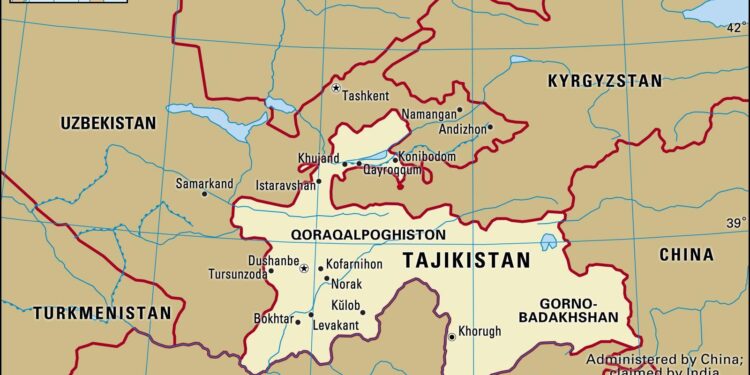
In a geopolitical landscape marked by shifting alliances and complex power dynamics, Tajikistan has emerged as an unexpected focal point in the tumultuous relationship between Russia, the Taliban, and the United States. Recent reports suggest a sinister scheme where Tajikistan, influenced by Russian interests, is allegedly orchestrating payments to the Taliban for targeting American forces in Afghanistan. This development not only raises significant concerns about regional stability but also complicates the already fraught interactions between Moscow and Washington. As Russia seeks to expand its influence in Central Asia and counterbalance U.S. presence in the region, its ties with the Taliban reveal a pragmatic, if controversial, approach to the new realities following the U.S. withdrawal from Afghanistan. This article delves into the implications of this alleged scheme, the motivations behind it, and what it means for the future of U.S. engagement in the region.
The Geopolitical Landscape of Tajikistan and Afghanistan
the tangled web of geopolitical interests surrounding tajikistan and Afghanistan reveals a precarious balance of power in Central Asia. The historic relationship between these two nations has become more complex following the U.S. withdrawal from afghanistan.Tajikistan, sharing a long border with Afghanistan, has been particularly sensitive to the risks posed by a resurgent Taliban and the potential for extremist movements spilling over its borders. the country’s leadership,wary of instability and insurrection,has sought to strengthen its ties with Russia,which may have ulterior motives in seeking to leverage its influence through support of the Taliban for targeted operations against American interests in the region.
The purported Russian scheme to financially incentivize the Taliban raises serious questions about the effectiveness of current U.S. strategies in the region and highlights a potential shift in the balance of power. Key factors influencing this scenario include:
- Presence of military bases and strategic partnerships in Central Asia
- Economic dependencies and trade agreements influencing Tajikistan’s policies
- The role of extremist groups in destabilizing both nations
Amidst these shifting alliances, a table of recent developments illustrates the evolving dynamics:
| Event | Date | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. Withdrawal from Afghanistan | August 2021 | Increased Taliban control |
| tajikistan’s military buildup | Ongoing | Enhanced border security |
| Reports of Russian payments to Taliban | 2023 | Increased tensions with the west |
These developments not only reshape regional politics but also pose significant challenges for international security frameworks as observers remain vigilant about the implications of such maneuvers. The stability of Central Asia hinges on the delicate equilibrium of these relationships, making it crucial for global powers to engage with both Tajikistan and Afghanistan in a manner that seeks to uphold regional stability rather than exacerbate existing conflicts.
Understanding the Russian Strategy Behind Taliban Engagement
The intricate relationship between Russia and the Taliban reveals a complex strategy aimed at leveraging the faction’s influence for regional power plays. Moscow perceives the Taliban not just as a militant group but as a potential ally in the broader grand chessboard of geopolitics. By fostering ties with the Taliban,Russia aims to counter the United States’ presence in Afghanistan and its implications for Central Asia. The strategic advantages for Russia include:
- Influence in Central Asia: Strengthening ties with Afghanistan to prevent extremist spillover into former Soviet states.
- Undermining U.S. Interests: utilizing the Taliban to act against American forces would exacerbate U.S. challenges in the region.
- Resource acquisition: Potentially accessing Afghanistan’s mineral wealth by aligning with the ruling group.
Furthermore, engaging with the Taliban serves a dual purpose; it positions Russia as a key player in regional stability while creating a counter-narrative against Western ideologies.By offering financial support and military assistance to the Taliban, Russia can cultivate a proxy force that enriches its influence without direct military intervention. This multifaceted engagement strategy can be summarized as follows:
| Strategic Goal | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|
| Counter U.S. Presence | Increased instability for American operations |
| Strengthen Regional Allies | Enhanced security for former soviet states |
| Access to Resources | Economic benefits from Afghanistan’s minerals |

Implications for U.S. Foreign Policy in Central Asia
The evolving dynamics in Central Asia, particularly the recent developments involving Tajikistan and the alleged Russian scheme to finance the Taliban for targeting Americans, present a complex challenge for U.S.foreign policy. As Afghanistan’s security situation continues to deteriorate, the ramifications extend far beyond its borders, affecting regional stability and U.S. interests. With Tajikistan’s strategic alignment possibly shifting under Moscow’s influence, washington must reassess its diplomatic and military engagement in Central Asia, prioritizing collaboration with local partners while countering adversarial influences. This situation underscores the necessity for a nuanced approach that not only addresses the immediate threats posed by terrorism but also considers the broader implications of U.S. withdrawal from Afghanistan.
To effectively navigate these tumultuous waters, U.S. policymakers should consider implementing the following strategies:
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties: Enhance diplomatic and economic relations with Central Asian nations to counterbalance Russian influence.
- Intelligence Sharing: Foster robust intelligence partnerships to monitor potential Taliban activities that threaten regional stability.
- Promoting security Cooperation: Develop joint military exercises and counter-terrorism initiatives tailored to address the specific challenges in the region.
Additionally, a thorough understanding of the regional dynamics is essential, especially the potential realignment of alliances. The table below outlines key players and thier positions concerning the U.S. interests in Central Asia:
| Country | Position | Potential Collaborations |
|---|---|---|
| Tajikistan | Possible alignment with Russia | Counter-terrorism training |
| Uzbekistan | Neutral, seeking economic ties | Infrastructure development projects |
| Kyrgyzstan | Security cooperation with the U.S. despite challenges | Joint military exercises |
Such a proactive stance can definitely help mitigate risks and maintain U.S. presence in a region vulnerable to external influences, ultimately leading to a more secure and stable Central Asia.

Evaluating Potential risks to American Personnel
the geopolitical landscape in Central Asia is increasingly complex, especially as Tajikistan develops closer ties with Russia amid rising tensions regarding the Taliban’s influence in Afghanistan. American personnel operating in or near the region face a multitude of risks as the possibility of a Russian scheme to fund Taliban activities targeting U.S. forces becomes more evident. Such operations could manifest in various forms, including direct attacks, intelligence gathering, and the use of proxies to undermine american interests.The likelihood of these threats necessitates a reevaluation of protective measures and strategies aimed at safeguarding the lives of those involved in diplomatic and military missions.
Identifying and assessing the possible consequences of this evolving dynamic is crucial. key risks associated with potential Russian maneuvers and Taliban actions include:
- Increased Hostility: A surge in anti-American sentiment among Afghan groups.
- Logistical Vulnerabilities: Compromised supply routes and operational capacities for U.S.forces.
- Coalition Strain: Tensions among allied nations working alongside the U.S. in the region.
| Risk Factor | Potential impact |
|---|---|
| Counterintelligence Failures | Heightened likelihood of ambushes and attacks. |
| Local Collaborations | Increased risk from local militias aligned with Taliban interests. |
Continued monitoring and proactive risk assessment are vital components in mitigating potential dangers to American personnel. The situation requires not only vigilance but also a coordinated response from intelligence agencies and military leaders to navigate this intricate threat landscape effectively.

The Role of Regional Powers in Counterterrorism Efforts
The involvement of regional powers like Tajikistan in counterterrorism efforts is often complex, intertwining geopolitical interests with local security challenges. One significant aspect to consider is the tacit agreement or understanding that some governments reach with non-state actors to manage threats on their soil. Tajikistan, strategically positioned near Afghanistan, has traditionally viewed the Taliban as a potential risk. Reports indicate that Tajikistan, in collaboration with Russia, may be exploring unconventional methods to mitigate this risk – potentially even by financially incentivizing the Taliban to target American interests in Afghanistan. This tactic raises questions about the ethical implications and effectiveness of engaging with such groups, which may undermine broader international counterterrorism initiatives and contribute to regional instability.
The dynamic of regional powers taking matters into their own hands reflects a shifting paradigm in international relations. Efforts by nations like Tajikistan can frequently enough seem like a short-term strategy that sacrifices long-term goals for immediate security gains. Some key factors influencing these regional counterterrorism efforts include:
- Proximity to Conflict Zones: Close geographical ties can lead to increased urgency in addressing threats.
- Balance of Power: Regional actors may act to maintain or shift the balance of power within their vicinity.
- Resource Allocation: Limited resources often dictate unconventional strategies, as states seek to safeguard their interests with minimal expenditure.
While these methods can yield swift results, they also risk entrenching violent non-state actors further in the region, complicating future diplomatic relations and counterterrorism operations. Such strategies exemplify the pragmatic yet precarious dance of regional politics, where the pursuit of stability can often conflict with broader principles of justice and international cooperation.

Recommendations for Strengthening U.S. Diplomatic Initiatives
To enhance U.S. diplomatic efforts in Central Asia and counter potential threats emanating from the region, a multi-faceted strategy is essential. First, the U.S. should increase its engagement with regional allies by organizing bilateral and multilateral forums that focus on shared security concerns. This can be achieved through:
- Regular high-level meetings with Central Asian presidents and defense ministers.
- Joint military exercises that emphasize counter-terrorism tactics.
- Developing intelligence-sharing agreements to facilitate quicker responses to threats.
Additionally, leveraging economic incentives to foster stability might prove beneficial. The U.S. can introduce development assistance packages aimed at promoting governance and economic growth in Central Asian nations. A detailed overview of potential initiatives could include:
| initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure Investment | Funding for roads and telecommunications to boost trade. |
| Education Programs | Scholarships for local students to study in the U.S. |
| Energy Cooperation | Collaborative projects focusing on renewable energy. |
Concluding Remarks
the intricate web of geopolitical maneuvering surrounding Tajikistan, Russia, and the Taliban underscores the increasingly complex landscape of international relations in Central Asia. As allegations emerge regarding Russia’s purported scheme to use the Taliban against American interests in Afghanistan, the implications for regional stability and security cannot be overstated.Such developments not only highlight the shifting alliances and rivalries in the region but also raise pressing questions about the future of U.S. involvement in Afghanistan and the broader implications for global counterterrorism efforts. As these dynamics continue to unfold, it is essential for policymakers and analysts alike to remain vigilant and informed, navigating the challenges posed by an evolving theater of conflict where both state and non-state actors play crucial roles. The situation demands a careful examination of motivations, strategies, and the potential for unforeseen consequences as world powers recalibrate their positions in this tumultuous region.