In the face of escalating climate challenges and increasing threats to biodiversity, effective forest management has never been more crucial. The Caucasus, Central Asia, and Türkiye are at the forefront of these environmental challenges, where diverse ecosystems, rich in wildlife and resources, confront the dual perils of deforestation and wildfires. Recognizing the urgent need for enhanced data collection and fire management strategies, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) has launched initiatives aimed at fortifying the resilience of these vital landscapes. This article delves into the FAO’s extensive efforts to strengthen forest monitoring and fire response mechanisms in the region, shedding light on the innovative approaches being adopted to safeguard our forests, promote enduring practices, and encourage regional cooperation in the face of an uncertain ecological future. As the stakes rise, so too does the obligation to ensure that forest ecosystems continue to thrive for generations to come.
Enhancing Forest Data Collection Methodologies in the Caucasus and Central Asia
In the diverse landscapes of the Caucasus and Central Asia, enhancing methodologies for forest data collection is pivotal for sustainable management and conservation efforts. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) emphasizes a multi-faceted approach that incorporates advanced technologies such as remote sensing, geographic details systems (GIS), and citizen science initiatives. By engaging local communities in monitoring efforts, the initiative fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, encouraging participatory data collection practices that provide real-time insights into forest health.This strategy not only enhances data accuracy but also builds local capacities and promotes awareness around forest management issues.
Moreover, the integration of these methodologies into fire management systems signifies a significant advancement. Utilizing automated fire risk assessments and predictive modeling tools enables timely interventions,mitigating potential disasters. The development of a shared database across nations facilitates collaboration and information exchange, ensuring that policymakers and forest managers can make informed decisions.Key components of this initiative include:
- Standardized data collection protocols to ensure consistency across regions.
- Training workshops aimed at enhancing technical skills in data analysis and interpretation.
- Collaborative platforms for sharing findings and best practices among stakeholders.

Innovative Technologies for Effective Fire Management Strategies
The integration of advanced technologies is revolutionizing fire management practices in forested regions. Remote sensing is at the forefront, utilizing satellite imagery and drones to gather real-time data on vegetation health, moisture levels, and temperature variations. This technology enables organizations to pinpoint areas at risk of wildfires, providing a proactive approach to fire prevention. Moreover, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) can analyse spatial data, helping to map high-risk zones and optimize resource allocation during fire events. By leveraging these tools, fire management teams can make informed decisions that enhance their preparedness and response strategies.
In addition to remote sensing and GIS, the request of artificial intelligence (AI) holds great promise for predicting and managing fire incidents. Machine learning algorithms can analyze ancient fire data, weather patterns, and land use changes, delivering insights that drive strategic planning efforts. Other innovations, such as mobile applications for community engagement, allow citizens to report smoke sightings or suspicious activities, establishing a grassroots approach to fire monitoring. The convergence of technology and traditional ecological knowlege empowers local stakeholders, ensuring a comprehensive response to fire management challenges in the region.
Collaboration Among Stakeholders: A Key element for Success
Collaboration among stakeholders is essential in enhancing forest data collection and fire management strategies in the Caucasus,Central Asia,and Türkiye. A multifaceted approach brings together local communities, governmental agencies, NGOs, and international organizations, ensuring all voices are heard and contributing to a more unified response to forest challenges. Together, these stakeholders can leverage their unique insights and expertise, wich can lead to more effective methodologies for data gathering and the implementation of fire management systems. Effective communication channels between these parties facilitate the sharing of knowledge, technology, and resources, empowering local communities while enhancing the overall resilience of forest ecosystems.
Key strategies for fostering this collaborative spirit include:
- Joint Training Programs: Organizing workshops and training sessions that bring together various stakeholders to build capacity in data collection techniques and fire management practices.
- Shared Platforms for Data Exchange: Creating digital platforms where stakeholders can access and share crucial data, making it easier to monitor forest conditions and fire risks.
- Policy Advocacy: Collaborating to advocate for supportive policies and frameworks that promote sustainable forest management and fire prevention practices.
- Regular Stakeholder Meetings: Holding frequent consultations to discuss ongoing projects, challenges, and successes, reinforcing the network of partners committed to forestry health.

Building Capacity and Training for Local Communities in Forest Conservation
Empowering local communities is crucial for the effective stewardship of forest resources. Through targeted capacity-building initiatives, local populations can gain the necessary skills to engage in sustainable forest management and conservation practices. Training programs focus on various aspects, including:
- Data collection techniques for accurate monitoring of forest health
- Fire management strategies tailored to regional ecosystems
- Community-lead initiatives promoting awareness of biodiversity
- Development of local advisory groups to facilitate ongoing education
The integration of traditional ecological knowledge with modern scientific methods creates a robust framework for conservation efforts. Workshops, field training, and collaboration with local NGOs foster a sense of ownership among community members. A recent study highlighted the impact of such programs, demonstrating that areas with trained local leaders saw a 50% reduction in forest fires. The following table summarizes these findings:
| indicator | Before Training | After Training |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Fires | 40 | 20 |
| Community Engagement (%) | 30% | 70% |
| Biodiversity Awareness (%) | 25% | 65% |

Policy Recommendations for Sustainable Forest Management Practices
To enhance the sustainability of forest management practices in the Caucasus, Central Asia, and Türkiye, it is essential to adopt a multi-faceted approach that prioritizes both ecological health and socio-economic benefits. Strengthening collaboration between government agencies, local communities, and non-governmental organizations can result in the formulation of effective policies that focus on the sustainable use of forest resources. Recommended actions include:
- Investment in Forest Data Collection: Deploy advanced technologies such as remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS) to improve data accuracy and availability.
- Community-Based Management Initiatives: Engage local populations in forest stewardship to align conservation efforts with community needs.
- Regulatory Reform: Create clear regulatory frameworks that encourage sustainable forestry practices while integrating traditional ecological knowledge.
Furthermore,a robust fire management strategy is vital for preserving forest ecosystems in these regions. This requires not only timely prevention and response protocols but also community education on fire risks. Key recommendations include:
- Integrated Fire Management Plans: Develop collaborative frameworks that involve all stakeholders in fire risk assessment and planning.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Conduct workshops and training sessions to teach communities about fire prevention and sustainable land use practices.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Establish metrics to regularly assess fire management effectiveness and adapt strategies as necessary based on data-driven insights.
| Proposal | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Investment in Technology | Increased data accuracy and resource management |
| Community Engagement | Enhanced local stewardship and biodiversity preservation |
| Fire Prevention Training | Reduced wildfire risks and improved community resilience |
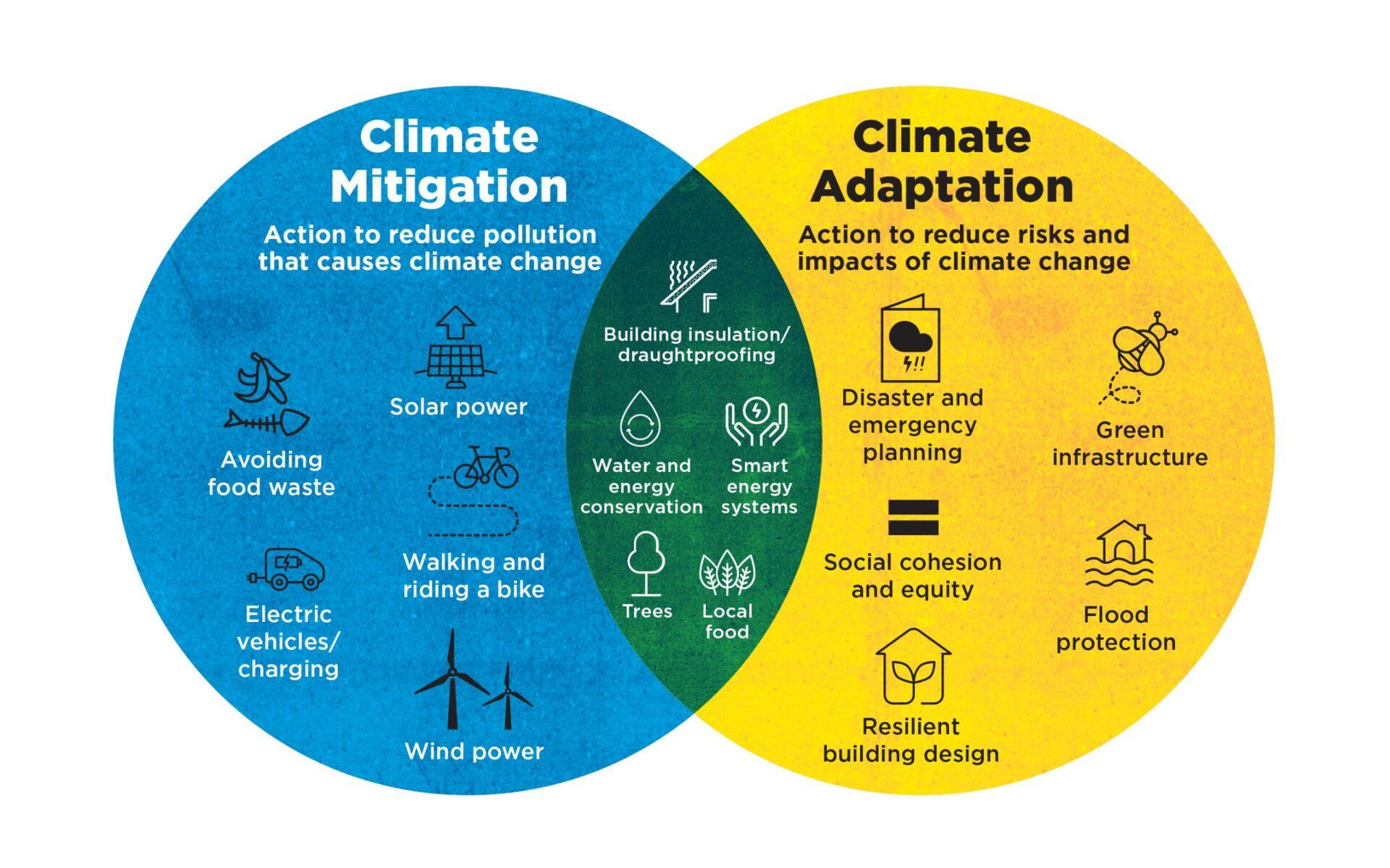
Integrating Climate Change Adaptation Measures in Fire Prevention Plans
Integrating climate change adaptation measures into fire prevention plans is crucial for enhancing resilience in forest ecosystems.By understanding the interplay between climate variations and fire risks, stakeholders can proactively develop strategies that mitigate potential damage. Key adaptation measures may include:
- Enhanced monitoring of climate trends: Regular assessment of weather patterns to forecast fire risks.
- Improved vegetation management: Adjusting forest management practices to maintain healthier ecosystems that are less susceptible to fires.
- Community engagement: Involving local communities in fire management strategies to promote awareness and collective action.
- Investment in infrastructure: Building firebreaks and access roads to facilitate quicker response times during emergencies.
additionally, collaboration among governments, NGOs, and local communities is vital for the effective implementation of these measures. By aligning fire management plans with regional climate adaptation policies, a more comprehensive approach can be achieved. The following table highlights some potential collaboration strategies:
| Strategy | Stakeholders Involved | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Training Programs | Authorities, NGOs, Local Communities | Increased knowledge and preparedness |
| Research Collaborations | Academic Institutions, Government Agencies | Improved data on fire risks and climate impacts |
| Public Awareness Campaigns | Non-profits, Community Leaders | Enhanced community readiness and response |
To Wrap It Up
As the challenges posed by climate change and increasing human activity continue to threaten the rich biodiversity and ecological balance of the Caucasus, Central Asia, and Türkiye, the imperative to enhance forest data collection and fire management becomes ever more critical. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations stands at the forefront of this vital initiative, harnessing advanced technologies and fostering regional collaboration to protect these valuable landscapes. By adopting comprehensive strategies that include improved monitoring systems, community engagement, and sustainable practices, stakeholders aim to build resilience against the looming threat of wildfires while ensuring the preservation of vital natural resources. Through these concerted efforts, the region not only seeks to safeguard its forests but also to secure the livelihoods of millions who depend on them. as we look to the future,the integration of robust data collection and proactive fire management will be essential in mitigating risks and promoting sustainable development across these diverse ecosystems.

















