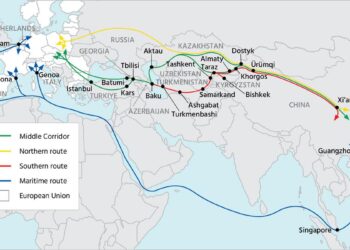
In an era where global connectivity is more crucial than ever, the aspiring infrastructure projects linking Asia to Europe stand as monumental testaments to human engineering and collaboration. CNN delves into the expansive network of gigantic tunnels and bridges that not only facilitate the movement of goods and people across continents but also symbolize the merging of cultures and economies. From the awe-inspiring lengths of the Bering Strait Tunnel proposal to the intricate designs of the Eurasian Land Bridge, these projects are reshaping trade routes and redefining geopolitical landscapes. As nations strive for enhanced cooperation and integration, this exploration sheds light on the challenges, innovations, and potential benefits tied to these colossal endeavors, drawing a vivid picture of a world increasingly interconnected by steel and concrete.
The Vision Behind Transcontinental Connectivity Initiatives
The ambitious projects aimed at connecting Asia and Europe through massive tunnels and bridges represent a remarkable shift in our approach to global infrastructure. By building these monumental links, nations hope to foster not just economic growth but also cultural exchange and mutual understanding. The underlying vision is to create a seamless network that facilitates trade and travel,erasing the geographical barriers that have historically separated these two vast continents. As investment flows into these engineering marvels, various stakeholders envision a future where logistics and connectivity are elevated to unprecedented levels, transforming local economies and enabling businesses to thrive on a transcontinental scale.
Moreover,these connectivity initiatives are set to prioritize sustainability and technological innovation. The design and construction of these projects emphasize environmentally amiable practices, such as using renewable energy sources and optimizing materials for longevity. Key features of this vision include:
- Smart Infrastructure: Utilizing IoT and AI to manage traffic and maintenance.
- Eco-friendly Transportation: Promoting rail and electric vehicles over conventional carbon-emitting options.
- Regional Collaboration: Strengthening ties between nations to streamline cross-border processes.
To track the progress of these initiatives and their potential impact, a simple overview can be found in the table below:
| Project Name | Location | status | Expected Completion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asia-Europe Tunnel | Turkey to Bulgaria | In Progress | 2025 |
| Transcontinental Bridge | Caspian Sea | Planned | 2028 |
| Bering Strait Link | Russia to Alaska | Feasibility Study | 2030 |

Engineering Marvels: The Design and Construction of Mega Infrastructure
As nations strive to enhance connectivity, the engineering feats of tunnels and bridges have emerged as beacons of human ingenuity. These colossal infrastructures, often dubbed as “the arteries of international trade,” not only facilitate the movement of goods and people but also symbolize the unification of diverse cultures. Some of the most remarkable structures include:
- The Channel Tunnel: Spanning 50 kilometers under the English Channel, this marvel drastically reduces travel time between the UK and continental Europe.
- The Eurasia Tunnel: Linking the Asian and European sides of Istanbul, this underwater tunnel has transformed urban transport dynamics.
- The Yavuz Sultan selim Bridge: Known as the third bridge over the Bosphorus, it stands as one of the widest and longest suspension bridges in the world.
Constructing these monumental structures requires not only elegant engineering techniques but also innovative materials capable of withstanding the challenges posed by geography and climate. As a notable example, the incorporation of self-healing concrete has increased longevity, while smart technologies allow for real-time monitoring of structural integrity.Below is a brief table showcasing some key features of notable bridges connecting Asia and Europe:
| Bridge/Tunnel | Location | Length (km) | Opened |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel Tunnel | England to France | 50 | 1994 |
| Eurasia Tunnel | Istanbul, Turkey | 14.6 | 2016 |
| Yavuz Sultan Selim Bridge | Istanbul, Turkey | 59.6 | 2016 |

Economic Impacts: How Tunnels and Bridges Transform Trade Relations
The construction of tunnels and bridges that connect Asia to Europe heralds a new era of economic synergy between these vast regions. These monumental infrastructures facilitate efficient transportation of goods and resources,substantially reducing travel time and costs. By creating seamless links, they enhance supply chain logistics, allowing businesses to operate more dynamically and respond swiftly to market demands. Key benefits include:
- Increased trade volume,as barriers to movement are diminished.
- Enhanced foreign investment opportunities due to improved access.
- Job creation in construction and operational sectors.
- Regional advancement, leading to economic growth in previously isolated areas.
Moreover, the establishment of these connections fosters stronger diplomatic ties and cooperation between Asian and European nations. Governments and businesses can collaborate more effectively, promoting an environment conducive to innovation and technology sharing. As a result, trade policies and agreements can evolve, benefiting countries involved in cross-border commerce. An illustrative overview of potential trade flows post-implementation could be represented as follows:
| Region | Expected Increase in Trade (in billion $) | New Trade Agreements |
|---|---|---|
| Asia | 150 | 5 |
| Europe | 120 | 3 |
| Middle East | 50 | 2 |

Environmental Considerations in Building Cross-Continental Links
as engineering feats such as cross-continental tunnels and bridges become increasingly viable,the environmental implications of such massive infrastructure projects cannot be overlooked.enduring design principles are now at the forefront of discussions among engineers, policymakers, and ecologists.Key considerations include:
- Wildlife migration: Assessing impact on habitat corridors to ensure animals can navigate landscapes disrupted by construction.
- Carbon Footprint: Implementing green technologies during construction to minimize emissions.
- Water Management: Utilizing techniques to protect local waterways from potential contamination.
Additionally, extensive environmental impact assessments (EIAs) play a crucial role in outlining the ecological footprint of proposed projects. By adopting best practices in construction and promoting community involvement, stakeholders aim to mitigate adverse effects. A recent comparative analysis highlights various mitigation strategies:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Reforestation | Planting trees to replace those lost to construction. |
| Wildlife Crossings | Building overpasses and underpasses for safe animal passage. |
| Renewable Energy Adoption | Using solar panels and wind turbines in construction sites. |

Future Prospects: Expanding the Network for Sustainable Development
As the world increasingly recognizes the need for sustainable development, the ambitious infrastructure projects spanning from Asia to Europe herald a new era of connectivity and collaborative growth. These colossal tunnels and bridges not only serve as physical structures but also symbolize the potential for integrated economic partnerships. By enhancing trade routes and minimizing transportation times, the initiative promotes the exchange of goods and services while reducing carbon footprints associated with traditional logistics methods.
Moreover, the expanding network encourages technological innovation as countries come together to share knowledge and best practices in sustainable construction and maintenance. This collaborative effort is expected to lead to the development of eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient transport systems, fostering a new age of green technology across nations. Regional stakeholders are poised to benefit from job creation, boosting local economies, while ensuring that environmental concerns are at the forefront of development strategies. Such initiatives usher in the potential for inclusive social progress, paving the way for a prosperous future.

Policy Recommendations for enhancing Cross-Border Collaboration
To strengthen the frameworks that support cross-border collaboration across Asia and Europe, it is indeed essential to adopt policies that prioritize connectivity and economic integration. This can be achieved through:
- Harmonizing Regulations: Establish common standards and regulations that facilitate smoother transportation and trade across borders.
- Investing in Infrastructure: Allocate funds for the development of crucial infrastructure, such as roads, railways, and ports, that connect major economic hubs.
- Encouraging Public-Private Partnerships: Foster collaborations between governments and private sectors to leverage resources and expertise in building and maintaining cross-border projects.
- Enhancing Digital Connectivity: Implement advanced digital infrastructure to support seamless communication and commerce between regions.
Moreover, cultivating an environment for diplomatic dialog is vital in addressing potential conflicts and optimizing collaborative efforts. Key initiatives could include:
- Regular Multilateral Meetings: Organize periodic conferences that bring together stakeholders from various countries to discuss challenges and opportunities.
- Establishing Joint Task Forces: Create specialized groups focused on addressing specific issues related to cross-border transportation and trade facilitation.
- Promoting cultural exchanges: Increase initiatives that encourage people-to-people connections to foster understanding and cooperation.
| Challenges | Proposed Solutions |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Barriers | Harmonize trade regulations |
| Infrastructure Gaps | Invest in key transport links |
| Lack of Communication | Enhance digital infrastructure |
| Geopolitical Tensions | Encourage diplomatic forums |

Concluding Remarks
the monumental infrastructure projects connecting Asia to Europe exemplify the power of engineering and international collaboration. These expansive tunnels and bridges not only facilitate the movement of goods and people, but also foster cultural exchange and economic growth across two diverse continents. As nations invest in these ambitious developments, the vision of a more interconnected world becomes increasingly tangible. The ongoing challenges, from environmental concerns to geopolitical tensions, underscore the complexities of such grand endeavors. Yet, the promise of greater unity and understanding between Asia and Europe remains a driving force behind these colossal constructions. As we look to the future, the continued progress of these vital links may very well shape the landscape of global connectivity for generations to come.