As Vietnam navigates a transformative period under its new regime, the intricate dance of economic reform, international relations, and domestic governance is shaping the country’s future trajectory. With a leadership that prioritizes both continuity and change,Vietnam is positioning itself to capitalize on emerging opportunities while addressing longstanding challenges. This article explores the key strategies and policies that define vietnam’s current governance, examining how the regime is working to solidify its footing in a rapidly evolving East Asian landscape. as regional dynamics shift and global economic realities fluctuate, understanding vietnam’s approach offers valuable insights into the broader implications for southeast asia and beyond.
Vietnam’s Political Landscape Under the New Regime
As Vietnam adapts to its new political regime, the landscape is marked by significant changes in governance and public policy. The leadership embraces a blend of socialist principles and market-oriented reforms, aimed at not only sustaining economic growth but also enhancing the quality of governance. Key features of this emerging political structure include:
- Centralized Leadership: The Communist Party continues to exert strong influence over political decision-making, ensuring ideological consistency while navigating modern challenges.
- Economic Reforms: Increasing integration into the global economy leads to a focus on attracting foreign investment and fostering entrepreneurship.
- Social Stability: Emphasis on maintaining harmony among diverse ethnic and social groups to prevent dissent and unrest.
In this rapidly evolving climate, the regime is also faced with pressing issues surrounding governance and civil rights. While economic progress remains a priority,there is growing scrutiny regarding the political freedoms of its citizens. The government aims to balance economic aspirations with the need for political legitimacy. To illustrate, here is a snapshot of the current political focus areas:
| Focus Area | Priority Actions |
|---|---|
| Corruption Prevention | Implement stricter regulations and promote transparency. |
| Civic Engagement | Encourage public discourse while managing dissent. |
| Environmental Policies | Develop enduring practices in response to climate change. |
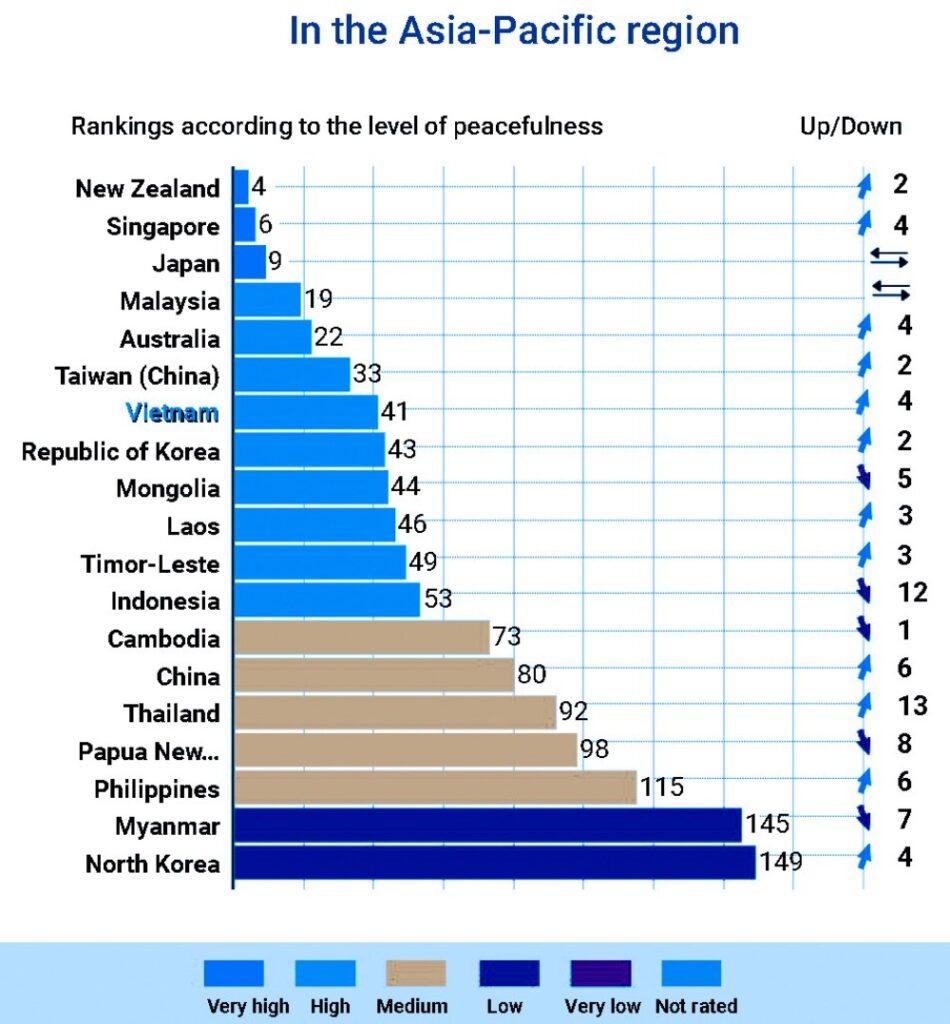
Economic Strategies for Sustainable Growth in Vietnam
In the context of its evolving economic landscape, Vietnam is poised to implement innovative strategies that promote sustainability while fostering growth. Key approaches include:
- Green Financing: Encouraging investment in renewable energy and sustainable projects through tax incentives and public-private partnerships.
- Digital Change: Leveraging technology to enhance productivity across sectors, prioritizing the development of e-commerce and smart agriculture.
- skill Development: Focusing on education and vocational training programs to prepare the workforce for emerging industries.
To support these strategies, the Vietnamese government is actively pursuing international collaboration. Such partnerships would not only bring in foreign direct investment but also facilitate knowledge transfer in sustainable practices. The government’s long-term vision can be encapsulated in the following table:
| Strategic Focus | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Initiatives | 30% share in national electricity consumption by 2030 |
| Investment in Technology | enhanced productivity and competitiveness in global markets |
| Skill Enhancement Programs | Reduction in unemployment rate and boosted GDP growth |

Navigating Regional Relationships in East Asia
In the complex tapestry of East Asian geopolitics, Vietnam’s new leadership is actively redefining its regional relationships. Under the stewardship of the recent regime, Vietnam is positioning itself as a cooperative player within the Association of Southeast Asian nations (ASEAN) while balancing its historical ties with China and strengthening its alliance with the United States. The government’s approach has included a multi-faceted strategy focused on enhancing economic partnerships and ensuring national security without overtly alienating major powers in the region. Key initiatives include:
- Strengthening Economic Ties: Bolstering trade agreements with ASEAN nations and the broader Indo-Pacific region.
- Security Collaborations: Engaging in defense dialogues and joint military exercises with the U.S. and allies to counterbalance Chinese influence.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Promoting people-to-people exchanges to foster mutual understanding and goodwill among nations.
the dynamism of vietnam’s foreign policy is particularly relevant as it navigates territorial disputes in the South China Sea and other regional security concerns. The newly formed government recognizes that Vietnam’s stability is intertwined with regional peace and collaborative frameworks. To track the evolving trends in Vietnam’s diplomatic engagement, it is indeed essential to consider the following factors shaping its relationships:
| Factor | Impact on Relations |
|---|---|
| China’s Assertiveness | Increased diplomatic balancing acts to navigate conflicts. |
| U.S. Strategic Rebalancing | Heightened military collaborations and economic partnerships. |
| ASEAN Unity | Strengthened collective bargaining power on regional issues. |

Human Rights and Civil Liberties: challenges Ahead
As Vietnam navigates its newfound political landscape, the intersection of governance and individual liberties faces significant scrutiny. critically, the suppression of dissent remains a pressing concern, with governmental actions continuing to target activists and independent media.Recent reports have detailed incidents where individuals advocating for reform have experienced surveillance, harassment, and imprisonment. This environment stifles democratic engagement and poses questions about the long-term sustainability of Vietnam’s political model in the eyes of both local citizens and the international community. Efforts to increase transparency could be overshadowed by stricter controls over civil liberties, which may hinder the nation’s ability to evolve amidst global expectations for human rights compliance.
Movements advocating for political reform are increasingly met with challenges in a climate that prioritizes stability over individual freedoms. The government’s cautious yet progressive reforms may indeed open up avenues for development,yet they must concurrently grapple with the reality that civil liberties cannot be sacrificed for economic gain. Organizations monitoring the situation in Vietnam highlight that increased grassroots mobilization demonstrates a populace eager for change, yet they also caution that state responses could lead to heightened repression. This dichotomy illustrates the complexities facing Vietnam, where the quest for economic advancement must contend with fundamental human rights issues.

Recommendations for Strengthening Vietnam’s International Standing
To enhance its global presence, Vietnam should consider a multifaceted approach that leverages both diplomatic and economic strategies. Strengthening regional partnerships is essential, particularly within ASEAN, where Vietnam can play a pivotal role in promoting stability and economic integration. The country should also seek to expand its ties beyond Southeast Asia, focusing on building strategic relationships with major economies such as the United States, japan, and the European Union. This could involve:
- enhancing trade agreements to foster economic interdependence.
- Participating actively in multilateral forums to amplify its voice on global issues.
- Pursuing diplomatic initiatives that address regional security concerns.
In tandem with diplomatic efforts, investment in innovation and technology will help position Vietnam as a competitive player on the world stage. By focusing on education and workforce development,Vietnam can cultivate a skilled labor force suited for the demands of a rapidly changing global market. Additionally, promoting sustainable practices in industry and agriculture will not only boost economic growth but also improve Vietnam’s environmental reputation, aligning with global sustainability goals. Key strategies should include:
| Strategy | description |
|---|---|
| Research & Development Investment | Allocate resources to foster innovation in key industries. |
| Enhancing Digital Infrastructure | Develop robust digital platforms to support commerce and education. |
| Green technology Promotion | Support initiatives that focus on renewable energy and sustainable practices. |

Insights and Conclusions
as Vietnam’s new regime navigates the complexities of both domestic policies and international relations, it is establishing a distinctive identity on the global stage.The leadership’s commitment to economic reform, coupled with a nuanced approach to diplomacy, reflects an adaptive strategy aimed at sustaining growth while addressing the challenges of governance and public accountability. Observers will be closely watching how these developments unfold in the context of regional dynamics and global geopolitics. As vietnam strives to solidify its footing, the implications of its policies will undoubtedly resonate beyond its borders, influencing not only local stakeholders but also broader East Asian relations. the path ahead might potentially be fraught with obstacles, yet it offers a unique opportunity for vietnam to assert its position as a significant player in the ever-evolving landscape of the region.

















