In a important development in global trade dynamics, Japan has issued a stern warning regarding teh implications of ChinaS recent export controls on critical semiconductor materials. As the world’s technological landscape becomes increasingly interconnected, the move by Beijing threatens to disrupt the supply chain of essential components pivotal to the manufacturing of advanced electronics. This warning underscores Japan’s strategic concerns amidst escalating tensions in the region and highlights the critical role that semiconductor materials play in national security and economic stability. In this article, we explore the nuances of china’s export restrictions, Japan’s response, and the potential repercussions for the global tech industry.
Japan’s National Security Concerns Rise Amid China’s Export Controls on Critical Chip Materials

As tensions escalate in East Asia, Japan’s government is expressing increasing alarm over China’s recent restrictions on the export of critical materials essential for semiconductor production. The decision by China to impose controls on materials such as gallium and germanium, which are vital for producing advanced chips, has prompted Japan to reconsider its own supply chains and national security strategies. Experts warn that these measures not only threaten Japan’s semiconductor industry but also challenge the broader stability of global tech markets, as many Japanese manufacturers rely heavily on these materials to maintain their competitive edge.
In response to these developments, Japan aims to bolster its domestic production capabilities and diversify its import sources to mitigate risks. Key initiatives include:
- Investment in local semiconductor fabrication plants, enhancing domestic supply of essential components.
- Strengthening partnerships with allied nations to create a cohesive supply chain that circumvents reliance on any single country.
- Incentivizing research and development in alternative materials and technologies to reduce dependence on conventional sources.
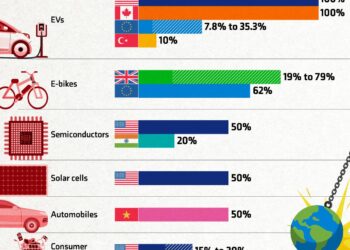
| Material | Importance | Current Supply Source |
|---|---|---|
| Gallium | Essential for high-speed electronics | China |
| Germanium | Used in fiber optics and solar cells | China |
Impacts on Global Semiconductor Supply Chains: How Japan’s Warning Reflects Wider Economic Risks

The recent alert from Japan regarding China’s export controls on semiconductor materials has far-reaching implications for global supply chains, particularly in the technology sector. As one of the key global players in semiconductor manufacturing, Japan is acutely aware that diverging regulatory landscapes can disrupt the balance of supply and demand. The situation has highlighted several critical concerns, including:
- Dependency Risks: Countries heavily dependent on imports for semiconductor materials could face production bottlenecks, leading to increased prices and longer lead times for essential components.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Heightening geopolitical tensions may result in retaliatory measures or further restrictions, exacerbating existing supply shortages.
- Investment Redirects: Companies may reconsider their supply chain strategies, possibly shifting investments towards alternative sourcing regions or seeking new suppliers in response to regulatory risks.
Moreover, the semiconductor industry’s unique characteristics compound these challenges. For instance, manufacturing processes for chips demand a delicate interplay of materials, equipment, and human expertise. disruptions in one area can have cascading effects, as illustrated in the table below:
| Component | Potential Impact of Disruption |
|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Increased costs & delayed production |
| Manufacturing Equipment | Longer cycles & reduced capacity |
| Logistics | Shipping delays & escalating expenses |
| Workforce | Skill shortages & increased labor costs |
Analyzing the Strategic Importance of Semiconductor Materials in Modern Technology
As global technological competition intensifies, the importance of semiconductor materials cannot be overstated. Nations are increasingly recognizing that these materials are not merely components of electronics but serve as the backbone for various high-tech industries. Japan’s recent warnings regarding China’s export controls on chip materials underscore a growing acknowledgment of the strategic implications inherent in this sector. The supply chain vulnerabilities posed by geopolitical tensions have led to serious concerns about access to essential materials, such as silicon, gallium, and germanium, which are critical in semiconductor manufacturing.
Within this landscape, several factors highlight the strategic meaning of semiconductor materials:
- National Security: Control over semiconductor production and materials influences a nation’s defense capabilities.
- Technological Sovereignty: Countries are striving for self-sufficiency to mitigate dependency on foreign suppliers.
- Economic Growth: The semiconductor industry is a key driver of innovation and economic competitiveness.
In light of these elements, countries like Japan are prioritizing policies that enhance domestic production while also building alliances to secure reliable supply chains. This strategic approach not only aims to safeguard national interests but also promotes a more resilient global technological ecosystem.
Potential Responses: What Japan and Its Allies Can Do to Mitigate Supply Chain Vulnerabilities

To address the growing concerns over supply chain vulnerabilities, Japan and its allies can adopt a multi-faceted strategy that emphasizes resilience and diversification. Key measures could include:
- Diversifying Sources: Actively seek alternative suppliers for critical materials to reduce dependency on a single country.
- Investment in Domestic Production: Enhance capabilities in semiconductor manufacturing and related technologies within national borders.
- Strategic stockpiling: Maintain reserves of essential materials to buffer against sudden supply disruptions.
- strengthening Alliances: Collaborate with like-minded nations to share resources and data on supply chain risks.
- Research and Development: Invest in R&D to innovate and find substitutes for sensitive materials currently sourced from China.
Moreover, establishing a robust regulatory framework that promotes openness and accountability in supply chains can play a crucial role. This could involve:
| Action Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Assessment Framework | Develop comprehensive guidelines for evaluating supply chain risks associated with foreign dependencies. |
| Incentives for Compliance | Create financial incentives for companies to comply with new regulations aimed at reducing supply chain risks. |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Facilitate collaboration between governments and the private sector to share knowledge and resources effectively. |
Future Implications for Japan-China relations in the Context of Technology and Trade

The evolving landscape of technology and trade between Japan and China presents significant implications for their bilateral relations. As Japan raises alarms over China’s recent export controls on critical chip materials, concerns about supply chain vulnerabilities deepen. The restrictions imposed by China could potentially limit Japan’s access to essential components for semiconductor production, which is vital for both nations’ tech industries. In response, we may see Japan accelerating its efforts to diversify supply sources, investing more heavily in domestic semiconductor capabilities, and strengthening partnerships with othre nations, particularly those within the Indo-pacific region. Key considerations for Japan include:
- Exploring alternative suppliers for chip materials
- Bolstering local semiconductor research and development initiatives
- Forming strategic alliances with allies in the tech sector
- Enhancing cybersecurity measures to protect intellectual property
The long-term repercussions of these developments could reshape the dynamics of Japan-China relations, driving both nations to reassess their economic interdependencies. While the immediate focus may be on mitigating risks associated with China’s export policies, there is also the possibility of increased innovation and competitiveness in Japan’s technology sector. This situation may prompt a technological rivalry that heightens the stakes for both countries. A comparison of potential scenarios illustrates the weight of these considerations:
| Scenario | Potential Outcome for Japan |
|---|---|
| Increased Export Controls from China | Greater urgency in pursuing self-sufficiency in semiconductor technology |
| Strengthening Alliances with Other Nations | Expansion of collaborative innovation and technology transfer |
| Increase in Domestic Investment | Long-term growth and resilience of Japan’s tech industry |
Navigating the Semiconductor Landscape: Recommendations for Policymakers and Industry Leaders
In the face of increasing geopolitical tensions, particularly regarding China’s control over semiconductor materials, both policymakers and industry leaders must take proactive steps to safeguard their interests. It is indeed vital to establish stronger supply chain resilience by diversifying raw material sources beyond volatile regions. Engaging in international partnerships can definitely help mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on a single country, thereby enhancing global competitiveness. Additionally, investing in domestic production capabilities and incentivizing local innovation will fortify national security and technological independence.
Policymakers shoudl also consider creating regulatory frameworks that promote transparency and safeguard intellectual property. This can be achieved through bilateral agreements that enforce fair trade practices and prevent unauthorized technology transfer. Moreover, fostering collaboration between government, academia, and the semiconductor industry can lead to innovative solutions to current supply chain vulnerabilities. Industry leaders, on their part, should prioritize research and development investments that focus on alternative materials and manufacturing techniques, ensuring the sector remains agile amidst evolving market conditions.
Final Thoughts
Japan’s heightened concerns regarding China’s recent export controls on semiconductor materials reflect a pivotal shift in the geopolitics of technology and trade. As nations scramble to secure their supply chains in an increasingly polarized environment,the implications of these restrictions extend far beyond the semiconductor industry,potentially reshaping global economic relations and innovation pathways. Japan’s proactive stance may serve as a catalyst for broader regional collaboration among allied nations, as they seek to mitigate risks and strengthen technological independence in the face of evolving threats. the unfolding situation will undoubtedly demand close scrutiny from policymakers, industry leaders, and analysts alike, as the balance of power continues to shift in the high-stakes arena of high-tech resources.