in the complex tapestry of international relations, the interplay between the United States and Yemen presents a striking case study of miscalculated strategies and unintended consequences.As the conflict in Yemen has escalated into one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises, analyzing America’s role in this tumultuous landscape reveals a series of policy decisions that many critics argue have contributed to the country’s descent into chaos. The article “Recipe for Failure: On the U.S. and Yemen,” published in The Hindu, delves into the historical context, examines the layers of diplomatic engagement, and highlights the repercussions of military support that, while aimed at stabilizing the region, often exacerbated local tensions. This exploration not only sheds light on the failures of U.S. foreign policy in Yemen but also serves as a cautionary tale for future interventions in geopolitical conflicts. As the world’s attention shifts to humanitarian needs and political resolutions,understanding the intricacies of this relationship is more crucial than ever.
The Historical Context of U.S. Involvement in Yemen

is deeply intertwined with the geopolitical complexities of the Middle East. Over the decades,Yemen has been a theater for Cold War rivalries,regional power struggles,and the enduring impact of colonial legacies. The U.S. initially engaged with Yemen in the context of containing Soviet influence, particularly during the civil wars in the 1960s and 1970s. This involvement continued into the 21st century, with U.S. policy increasingly focused on combating terrorism, particularly following the 9/11 attacks. The rise of Al-Qaeda in the arabian Peninsula (AQAP) prompted a shift in U.S. strategy, emphasizing drone strikes and counterterrorism operations that often disregarded the broader sociopolitical ramifications and the deeply rooted grievances of the Yemeni people.
Moreover, the U.S. has found itself increasingly enmeshed in Yemen’s internal conflicts, exemplified by its support for the Saudi-led coalition intervening in the Yemeni civil war since 2015. This intervention was justified on the grounds of restoring the internationally recognized government, yet it has led to a humanitarian disaster and a protracted conflict. The consequences of U.S. policy decisions in Yemen can be summarized as follows:
- Humanitarian Crisis: the conflict has resulted in one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises, with millions facing famine and disease.
- Regional Destabilization: U.S. actions have intensified regional rivalries, particularly between Iran and Saudi Arabia.
- Public Perception: The military intervention has eroded U.S. credibility and support in the region.
the Humanitarian Crisis: A Deepening Catastrophe
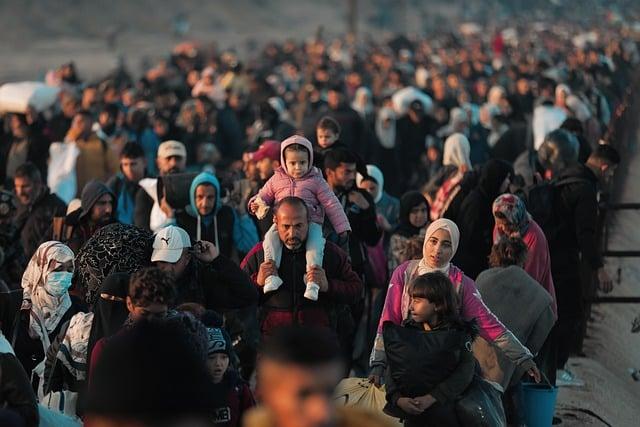

The ongoing humanitarian crisis in Yemen has become one of the moast pressing global issues, exacerbated by years of conflict and external intervention.Millions of civilians find themselves trapped in a cycle of violence, displacement, and instability, leading to a dire need for immediate humanitarian assistance.The war has decimated infrastructure, collapsing healthcare systems and limiting access to basic necessities. Key challenges include:
- Food Insecurity: Over 16 million people suffer from acute hunger, with many on the brink of famine.
- Healthcare Access: A staggering collapse of medical services has led to a resurgence of diseases, including cholera.
- Displacement: More than 4 million Yemenis have been forced to flee their homes, facing uncertain futures.
While international aid has been promised, the reality on the ground reveals a tragic disconnect between funding and effective delivery. Political disagreements among global powers often leave Yemen’s needs unaddressed, prolonging suffering and instability.Identifying key barriers to aid distribution is crucial, including:
| Barrier | Impact |
|---|---|
| Access Restrictions | Humanitarian workers face challenges due to ongoing conflict, hindering aid delivery. |
| Insufficient Funding | many aid programs are underfunded, limiting their reach and effectiveness. |
| political Interference | geo-political interests complicate humanitarian efforts,often prioritizing military strategy over civilian needs. |
Political Missteps: Analyzing the U.S. Strategy in Yemen

The strategic approach of the U.S. in Yemen has often been marked by a series of miscalculations that have not only exacerbated the humanitarian crisis but also undermined regional stability. Key factors contributing to this misstep include:
- Lack of a Clear Objective: the absence of a coherent strategy has left American involvement largely reactive rather than proactive.
- Support for Divisive Players: Aligning with disparate factions within Yemen has fueled internal divisions.
- Overreliance on Military Solutions: Prioritizing military intervention over diplomatic resolutions hinders enduring peace efforts.
Moreover, the impact of U.S. policies extends beyond immediate military implications, shaping long-term political landscapes. The Yemeni conflict serves as a microcosm of larger geopolitical rivalries, particularly between the U.S., Iran, and Saudi Arabia. The following table illustrates the main stakeholders and their influence in Yemen’s political landscape:
| Stakeholder | Role | Influence |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. | Military Support | High |
| Saudi Arabia | Coalition Leader | Very High |
| Iran | Support for Houthis | Medium |
| Houthis | Rebel Group | High |
Attempts at Diplomacy: Lessons from Failed Negotiations

Throughout the course of U.S. engagement in Yemen, significant attempts at diplomacy have yielded less than desired outcomes, often leading to a heightened cycle of conflict rather than resolution.The complexities of the Yemeni crisis can be attributed to a variety of factors, including divergence in interests among key local players, external influences from regional powers, and the often-overlooked humanitarian dimension of the conflict. The U.S. approach, traditionally centered on counterterrorism and stability, frequently sidelined the very voices essential for any sustainable peace agreement, namely those representing the Yemeni populace.
Analyzing these failed negotiations unveils critical lessons that could inform future diplomatic efforts not just in Yemen,but in similar conflict zones. Among the key takeaways are:
- Inclusivity is Crucial: Triumphant negotiations must prioritize the inclusion of all relevant stakeholders, particularly marginalized groups.
- Address Root Causes: Diplomatic initiatives must focus on underlying grievances that fuel conflict instead of merely addressing surface-level symptoms.
- Adapt to Local Contexts: A one-size-fits-all approach rarely works; understanding local dynamics is essential for effective diplomacy.
To illustrate the complexity of international negotiations, the following table outlines several distinct attempts made by the U.S.in the Yemeni context over the years:
| Year | Event | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | start of Saudi-led Intervention | Escalation of Conflict |
| 2018 | Stockholm Agreement | Temporary Ceasefire |
| 2020 | U.N. Talks | No Significant Progress |
Path Forward: Sustainable Solutions for Yemen’s Future

Amid the ongoing turmoil in Yemen, the need for sustainable solutions has never been more critical. The international community, especially the U.S., must reassess its strategies and prioritize long-term support that goes beyond immediate military or humanitarian aid. Sustainable solutions must focus on economic development, education, and infrastructure rebuilding to create a more stable and prosperous Yemen. Collaborative initiatives that include local governance will empower communities to rebuild from the ground up, addressing not only the symptoms of the conflict but tackling the root causes that have led to years of instability.
Implementing effective programs can yield transformative results. Consider the following approaches that are essential for fostering resilience in Yemen:
- Investment in Local Agriculture: Encouraging farmers to adopt sustainable farming practices can enhance food security.
- Educational Outreach: education initiatives that focus on vocational training for youth can provide skills necessary for job creation.
- Renewable Energy projects: Using solar and wind energy can definitely help rebuild communities while reducing dependency on external resources.
Strategies like these not only address immediate needs but also build the capacity for self-reliance, which is vital for Yemen’s long-term recovery.A structured approach to these solutions, underpinned by international support and collaboration with local entities, can usher in a new era of hope and sustainability.
The Conclusion
the complexities surrounding U.S. involvement in Yemen reveal a multifaceted challenge that extends beyond mere geopolitics. As highlighted throughout this article, the entrenched issues of humanitarian crises, regional instability, and the implications of foreign intervention have contributed to a situation that many now perceive as a recipe for failure. The U.S. has been caught in a cycle of conflicting interests, where the desire to exert influence is overshadowed by the dire humanitarian consequences faced by the Yemeni populace. Moving forward, it is indeed crucial for policymakers to reassess their strategies and prioritize diplomatic solutions that emphasize human rights and stability in the region. Only through a extensive and compassionate approach can there be hope for a more peaceful and prosperous Yemen, steering both the U.S.and the region away from further failure and towards sustainable resolution.